Introduction To .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950
The .NET Framework is a vital component of Windows, providing essential support for a multitude of applications and services. However, a frequent roadblock that Windows users encounter is the .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950. In this article, we look into the intricacies of this error and its resolution. We’ll explore the causes behind this issue, provide a step-by-step guide for troubleshooting, and suggest additional tips to tackle related problems. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge needed to mend this error and ensure the seamless functioning of your Windows system. Let’s start our journey into the world of .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950 solutions.
What is .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950?
The .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950 is a Windows issue that can be quite perplexing for users. This error code indicates a problem with the installation or activation of the .NET Framework 3.5, a crucial component for many applications and services in Windows.
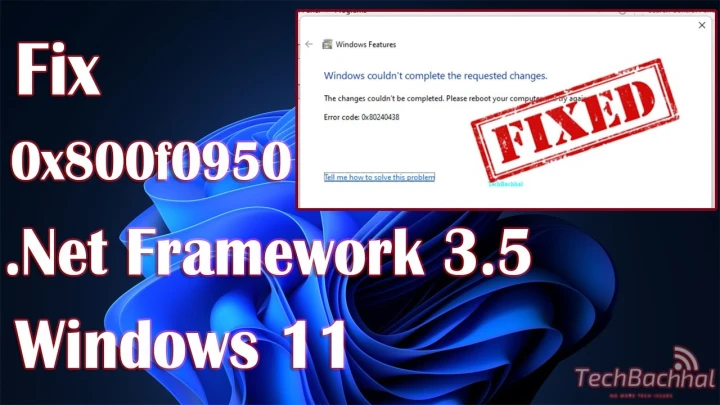
This error typically emerges when users try to enable or install the .NET Framework 3.5, often as a prerequisite for certain applications or legacy software. The 0x800F0950 error code can stem from several sources, including corruption in the Windows Component Store or issues with the installation source.
When this error strikes, it can result in the inability to run applications requiring the .NET Framework 3.5, potentially hindering your ability to utilize essential software. In this article, we’ll explore the various reasons behind the error, and provide you with the insights and solutions necessary to overcome it and restore your Windows system to its full functionality.
Common Causes of Error
The .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950 can manifest due to a multitude of underlying factors, often intertwined in complex ways. Here are some common causes contributing to this error:
- Missing or Corrupted System Files: The .NET Framework relies on a range of system files to function correctly. If any of these files are missing or corrupted, it can lead to the error 0x800F0950.
- Windows Update Issues: This error can sometimes result from problems with the Windows Update feature. Incomplete or failed updates may disrupt the installation or activation of the .NET Framework 3.5.
- System Misconfigurations: Incorrect configurations in your Windows system settings can interfere with the .NET Framework’s installation. Misconfigured group policies, for instance, can be a potential culprit.
- Software Conflicts: Existing software on your computer can conflict with the .NET Framework, resulting in the error. This often occurs when multiple software applications demand different versions of the framework.
- Malware Infections: Malware can cause significant system disruptions, including corrupting the .NET Framework 3.5 installation or activation.
By understanding these potential causes, you’re better equipped to navigate the troubleshooting and resolution process for the .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950. In the forthcoming sections of this article, we’ll delve into the steps required to resolve this issue and get your Windows system back on track.
Step by Step Guide to Resolve the Issue
Navigating the labyrinth of the .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950 can be a daunting task, but with a systematic approach, you can successfully resolve it. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you troubleshoot and fix this error:
Check Windows Update
Ensure that your system is up to date. Sometimes, missing updates can disrupt the .NET Framework installation. Go to “Settings” > “Update & Security” > “Windows Update” and check for any pending updates.

Use DISM
The Deployment Imaging Service and Management Tool (DISM) can help repair Windows images, including the .NET Framework components. Open a Command Prompt as an administrator and run the following command:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:NetFx3 /All /LimitAccess /Source:<path_to_windows_installation_media>
Replace <path_to_windows_installation_media> with the path to your Windows installation media or the “sources” folder on your installation media.
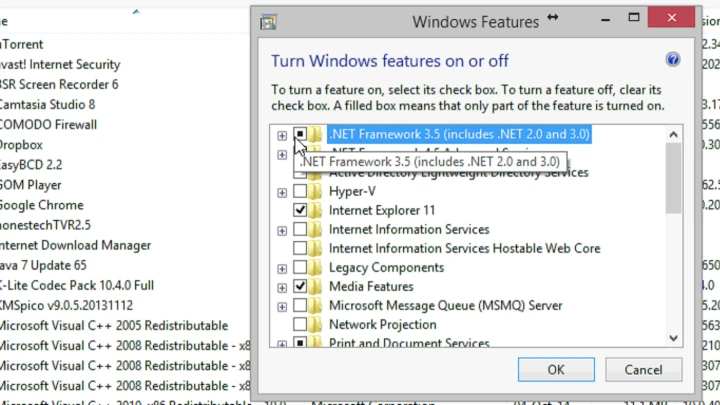
Enable .NET Framework 3.5
You can enable .NET Framework 3.5 from Windows Features. Go to “Control Panel” > “Programs” > “Turn Windows features on or off,” then check the box for “.NET Framework 3.5.”
Install .NET Framework 3.5 from Installation Media
If you have a Windows installation media, you can use it to install the .NET Framework 3.5. Insert the media, open Command Prompt as an administrator, and run:
dism /online /enable-feature /featurename:NetFX3 /All /Source:D:\sources\sxs /LimitAccess
Replace “D:” with your media drive letter.
Use Group Policy
If you’re on a network managed by Group Policy, your administrator might need to enable the feature for you.
Reboot and Verify
After applying any of these methods, restart your computer and check if the .NET Framework 3.5 is now functioning without error.
Remember, during this process, it’s essential to be patient and follow the steps meticulously. Sometimes the repair process may take some time, especially when using DISM. By diligently following these steps, you can successfully resolve the .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950 and ensure your Windows system is fully optimized. In other cases, if the aforementioned issue is caused by some internal system issues or errors, you can fix those using a suggested here system repair app.
2. Click Install and Scan Now to find all system issues causing the current problem.
3. Click Fix, Clean & Optimize Now to fix issues affecting your computer’s security and performance.
How to Prevent the issue in Future?
To prevent the reoccurrence of the .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950 and maintain a smooth-running Windows system, consider these key practices:
A. Regular Windows Updates
Stay vigilant with Windows Updates. Consistently applying updates helps to keep your system in good health, ensuring you have the latest patches and features. Also, remember to enable the installation of optional updates as the .NET Framework updates are sometimes included in optional packages.
B. System Maintenance
Perform routine system maintenance, including disk cleanup, defragmentation, and regular antivirus scans. This can help to prevent errors by ensuring that your system operates at its best.
C. Create System Restore Points
Before making significant changes to your system, such as installing software or performing system updates, create a system restore point. This is like a safety net that allows you to roll back your system to a previous state if anything goes wrong during the process.

By following these preventative measures, you can help ensure the stability of your Windows system and reduce the likelihood of encountering the .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950 in the future.
Conclusion
Resolving the .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950 is crucial for maintaining a healthy and efficient Windows operating system. This error, which can stem from multiple causes, can hinder your ability to run essential applications and services. However, with the right troubleshooting steps and a systematic approach, you can address this issue effectively.
This article has provided insights into the nature of the error, its common causes, and step-by-step solutions to rectify it. By following these guidelines and considering preventative measures, you can ensure a seamless Windows experience with a functional .NET Framework 3.5. Moreover, practicing routine system maintenance, regular software updates, and the creation of system restore points will minimize the risk of encountering this error in the future, contributing to the overall stability and performance of your Windows system. With these strategies in place, you can tackle the .NET Framework 3.5 Error 0x800F0950 and enjoy a more trouble-free computing experience. If you have any question, you can click to Visit Our Discussion Board.

Nishant Verma is a senior web developer who love to share his knowledge about Linux, SysAdmin, and more other web handlers. Currently, he loves to write as content contributor for ServoNode.




