Quick and Easy Ways to Access Task Scheduler in Windows 10 & 11
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- What is Task Scheduler?
- Why Use Task Scheduler?
- Easy Ways to Open Task Scheduler
- Using Run
- Using Command Prompt (CMD)
- Using Windows Search
- Using Control Panel
- Using Windows Settings
- Using PowerShell
- Real-World Applications of Task Scheduler
- Best Practices for Using Task Scheduler
- Troubleshooting Task Scheduler Issues
- Case Studies
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of technology and productivity, Task Scheduler in Windows 10 and 11 emerges as a powerful tool that allows you to automate tasks on your computer. Whether it's running a backup at a specific time or launching an application, knowing how to access this handy utility can save you time and effort. This guide provides comprehensive methods to open Task Scheduler easily and efficiently.
What is Task Scheduler?
Task Scheduler is a Microsoft Windows component that allows users to schedule the launch of programs or scripts at pre-defined times or after specified time intervals. It is an essential utility for managing automated tasks and ensuring your system runs smoothly.
Why Use Task Scheduler?
With Task Scheduler, users can:
- Automate routine tasks such as disk cleanup, backups, and software updates.
- Run scripts or applications at startup or during specific times.
- Improve productivity by reducing manual intervention.
Easy Ways to Open Task Scheduler
Now that you understand the importance of Task Scheduler, let’s explore various ways you can access it in Windows 10 and 11.
Using Run
One of the quickest ways to open Task Scheduler is through the Run dialog:
- Press Windows + R on your keyboard to open Run.
- Type
taskschd.mscand hit Enter.
Using Command Prompt (CMD)
Another efficient method is through the Command Prompt. Here’s how:
- Open Command Prompt by searching for it in the Start Menu or by pressing Windows + X and selecting Command Prompt.
- Type
taskschd.mscand press Enter.
Using Windows Search
Accessing Task Scheduler via Windows Search is straightforward:
- Click on the Search icon on the taskbar or press Windows + S.
- Type Task Scheduler in the search box and select it from the results.
Using Control Panel
You can also find Task Scheduler in the Control Panel:
- Open Control Panel by searching for it in the Start Menu.
- Select System and Security.
- Click on Administrative Tools.
- Find and select Task Scheduler.
Using Windows Settings
For Windows 11 users, Task Scheduler can be accessed through Settings:
- Open Settings by pressing Windows + I.
- Select System, then go to About.
- Click on Advanced system settings.
- In the System Properties window, click on Task Scheduler.
Using PowerShell
PowerShell provides another route to open Task Scheduler:
- Open PowerShell by searching for it in the Start Menu or pressing Windows + X and selecting Windows PowerShell.
- Type
taskschd.mscand press Enter.
Real-World Applications of Task Scheduler
Businesses and individuals alike leverage Task Scheduler for various applications:
- Automated Backups: Schedule periodic backups of critical data.
- System Cleanup: Automate cleanup tasks to optimize system performance.
- Email Reminders: Set tasks to send out reminders for meetings or deadlines.
Best Practices for Using Task Scheduler
To maximize the effectiveness of Task Scheduler, consider the following best practices:
- Always test tasks to ensure they run as expected.
- Use descriptive names for tasks to easily identify their purpose.
- Regularly review and update scheduled tasks to align with current needs.
Troubleshooting Task Scheduler Issues
Sometimes, tasks may fail to run as scheduled. Here are steps to troubleshoot:
- Check task history for error messages.
- Ensure the task is enabled and triggers are correctly configured.
- Make sure the computer is on and not in sleep mode when the task is scheduled to run.
Case Studies
Many individuals and companies have successfully utilized Task Scheduler to streamline their operations:
Case Study 1: A Small Business
A small retail business used Task Scheduler to automate their inventory reports, resulting in a 30% time saving for their staff.
Case Study 2: Freelancers
Freelancers have successfully used Task Scheduler to automate client follow-ups, improving client engagement significantly.
Conclusion
Task Scheduler is an underutilized feature in Windows that can significantly enhance productivity. By utilizing the methods outlined in this guide, you can easily access Task Scheduler, set up automated tasks, and improve your overall efficiency.
FAQs
1. What is Task Scheduler used for?
Task Scheduler is used to automate the launching of programs or scripts at pre-defined times or after specified intervals.
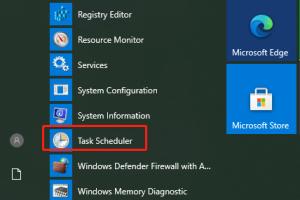
2. How do I open Task Scheduler using the Start Menu?
Type "Task Scheduler" in the Start Menu search bar and select it from the results.
3. Can Task Scheduler run tasks even when my computer is off?
No, the computer must be on for scheduled tasks to run unless you set a wake timer.
4. Is Task Scheduler available in Windows 10 and 11?
Yes, Task Scheduler is available in both Windows 10 and 11.
5. Can I schedule tasks for specific days of the week?
Yes, you can set tasks to run on specific days and times using the Task Scheduler interface.
6. What types of tasks can I automate with Task Scheduler?
You can automate a variety of tasks, including backups, software updates, and system maintenance.
7. How do I troubleshoot a failed task?
Check the task history for error messages and verify that the triggers, conditions, and settings are correct.
8. Is it safe to use Task Scheduler?
Yes, Task Scheduler is a built-in Windows feature and is safe to use for automating tasks.
9. Can I create multiple tasks in Task Scheduler?
Yes, you can create as many tasks as you need, each with its own triggers and settings.
10. What should I do if my scheduled task isn't running?
Ensure your computer is awake, check the task settings, and verify that the task is enabled.