Step-by-Step Guide to Enabling Active Directory in Windows 10
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- What is Active Directory?
- Requirements to Enable Active Directory
- Step-by-Step Guide to Enable Active Directory
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Case Studies and Real-World Applications
- Expert Insights
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Introduction
Active Directory (AD) is a crucial component for managing networks in Windows environments. Understanding how to enable and configure it in Windows 10 can significantly enhance your organizational capabilities. This guide will walk you through the process, provide expert insights, and share troubleshooting tips.
What is Active Directory?
Active Directory is a directory service developed by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It is used for managing computers and other devices on a network. AD provides a variety of network services, including:
- Authentication and authorization
- Directory services
- Group Policy management
- Single Sign-On (SSO)
Understanding AD is vital for IT professionals, especially those working in larger organizations where user management and security are paramount.
Requirements to Enable Active Directory
Before you can enable Active Directory in Windows 10, ensure you meet the following requirements:
- A Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, or Education edition installed
- Administrative privileges on the computer
- A stable internet connection for downloading any necessary components
Step-by-Step Guide to Enable Active Directory
Step 1: Access Windows Features
To get started, you need to access the Windows Features menu:
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard.
- Type Control Panel and hit enter.
- Select Programs.
- Click on Turn Windows features on or off.
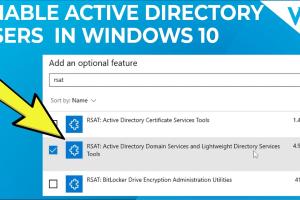
Step 2: Install Active Directory Domain Services
Follow these steps to install Active Directory Domain Services:
- In the Windows Features dialog, scroll down and check the box for Active Directory Domain Services.
- Click OK and allow Windows to install the necessary components.
Step 3: Promote Your PC to a Domain Controller
Once AD DS is installed, you need to promote your PC to a Domain Controller:
- Open the Server Manager from the Start menu.
- Click on Notification and select Promote this server to a domain controller.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to set up your new domain.
Step 4: Configure Active Directory
After promoting your PC, you will need to configure Active Directory:
- Open the Active Directory Users and Computers management console.
- Create user accounts, groups, and organizational units as needed.
Step 5: Verify Installation
Ensure that Active Directory is functioning correctly:
- Open the command prompt and type dsquery user.
- If correctly installed, you should see your domain users listed.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Enabling Active Directory can sometimes lead to common issues. Here are tips for troubleshooting:
- Installation Fails: Ensure your Windows version is compatible.
- Domain Join Issues: Check network connectivity and DNS settings.
- Permission Errors: Verify administrative privileges.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Many organizations have successfully implemented Active Directory to streamline their IT operations. Below are a few case studies demonstrating its effectiveness:
Case Study 1: Medium-Sized Business
A medium-sized business used Active Directory to manage over 200 employees. By implementing group policies, they were able to secure sensitive data and reduce IT support tickets by 30%.
Case Study 2: Educational Institution
An educational institution integrated Active Directory to facilitate student and staff access to shared resources. This led to improved collaboration and a 40% increase in resource usage.
Expert Insights
Experts recommend regularly updating your Active Directory environment and conducting audits to ensure compliance and security. Leveraging tools like PowerShell can also automate many routine tasks, enhancing efficiency.
FAQs
1. What is Active Directory used for?
Active Directory is used for managing computers, users, and resources within a network, providing authentication and authorization services.
2. Can I enable Active Directory on Windows 10 Home?
No, Active Directory can only be enabled on Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, or Education editions.
3. Do I need a server to use Active Directory?
Yes, typically Active Directory is used in conjunction with a Windows Server environment.
4. What are the benefits of using Active Directory?
Benefits include centralized user management, enhanced security, and improved resource allocation and access control.
5. How do I manage users in Active Directory?
You can manage users through the Active Directory Users and Computers management console.
6. Is Active Directory necessary for small businesses?
While not necessary, it can greatly simplify user management and security for small businesses as they grow.
7. Can Active Directory be used with non-Windows operating systems?
Yes, Active Directory can be integrated with Linux and macOS systems via LDAP.
8. How often should I back up Active Directory?
Regular backups are recommended, with at least a monthly backup for critical environments.
9. What is Group Policy in Active Directory?
Group Policy allows you to define security settings and manage user and computer configurations across the network.
10. Can I disable Active Directory after enabling it?
Yes, but disabling Active Directory may lead to loss of access to resources and requires careful planning.
Conclusion
Enabling Active Directory in Windows 10 is a powerful step towards efficient network management. By following the steps in this guide and addressing common challenges, you can optimize your organization's IT infrastructure.