Mastering Parallel Circuits: A Comprehensive Guide to Creation and Application
-
Quick Links:
- 1. Introduction to Parallel Circuits
- 2. Understanding Parallel Circuits
- 3. Components Required for a Parallel Circuit
- 4. Step-by-Step Guide to Making a Parallel Circuit
- 5. Applications of Parallel Circuits
- 6. Troubleshooting Common Issues in Parallel Circuits
- 7. Case Studies on Parallel Circuit Applications
- 8. Expert Insights on Circuit Design
- 9. Conclusion
- 10. FAQs
1. Introduction to Parallel Circuits
Parallel circuits are a fundamental aspect of electrical engineering and DIY electronics. Unlike series circuits, where components are connected one after the other, parallel circuits allow for multiple paths for current to flow. This characteristic offers unique advantages in both functionality and safety. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of creating parallel circuits, exploring their applications, troubleshooting tips, and expert insights.
2. Understanding Parallel Circuits
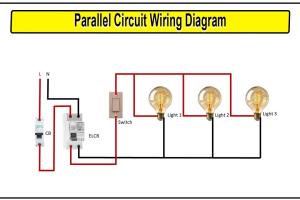
A parallel circuit consists of two or more components connected across the same voltage source, creating multiple pathways for the current. This design means that if one component fails, the others can still operate, enhancing the reliability of the circuit.
- Voltage: The voltage across each component remains the same.
- Current: The total current is the sum of the currents through each component.
Understanding these principles is crucial for both beginners and advanced users who wish to design effective electrical systems.
3. Components Required for a Parallel Circuit
To construct a simple parallel circuit, you will need the following components:
- Power Source: A battery or power supply providing the necessary voltage.
- Conductors: Wires to connect the components.
- Load Components: Resistors, LEDs, or any other devices you want to power.
- Switch: Optional, for controlling the circuit.
Gathering these components ensures a smooth building process for your parallel circuit.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Making a Parallel Circuit
Follow these steps to create your own parallel circuit:
- Step 1: Prepare Your Workspace
Ensure you have a clean, organized workspace with all your components within reach.
- Step 2: Connect the Power Source
Connect the positive terminal of your power source to one side of the circuit.
- Step 3: Attach Load Components
Connect each load component to the power source, making sure each one has its own path to the negative terminal.
- Step 4: Ensure Proper Connections
Double-check that all connections are secure and that there are no short circuits.
- Step 5: Test the Circuit
Power on the circuit and test each component to ensure they function properly.
This simple guide enables you to create a basic parallel circuit efficiently.
5. Applications of Parallel Circuits
Parallel circuits have various applications in daily life and industry. Some prominent examples include:
- Home Wiring: Most household electrical systems use parallel wiring to ensure that devices can independently operate.
- Battery Packs: Parallel configurations in battery packs allow for increased current capacity.
- LED Lighting: Parallel connections in LED circuits ensure uniform brightness and reliability.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues in Parallel Circuits
Even the simplest circuits can encounter issues. Here are some common problems and solutions:
- Component Failure: If one component fails, it can often be replaced without affecting others.
- Short Circuits: Ensure that your connections are not touching each other unintentionally.
- Voltage Drops: Check for proper connections and component ratings if you notice decreased performance.
7. Case Studies on Parallel Circuit Applications
Real-world applications of parallel circuits abound. For instance, in a residential setting, homeowners may install multiple light fixtures in parallel to ensure that if one bulb burns out, the others remain lit. This case illustrates the reliability of parallel circuits in everyday use.
Another example includes solar panel systems, where multiple panels are connected in parallel to increase the total current output while maintaining the same voltage.
8. Expert Insights on Circuit Design
According to electrical engineering experts, understanding the principles of parallel circuits is essential for anyone involved in electronics. Author and educator Dr. Jane Smith emphasizes the importance of experimentation: “Building circuits is not just about following instructions; it’s about understanding how components interact.”
9. Conclusion
Creating a parallel circuit is a valuable skill for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics. By understanding the principles behind parallel circuits, gathering the right components, and following a systematic approach, anyone can successfully build and troubleshoot their own circuits.
10. FAQs
What is a parallel circuit?
A parallel circuit is an electrical circuit that connects multiple components across the same voltage source, allowing current to flow through multiple paths.
What are the advantages of parallel circuits?
Advantages include reliability, as one component's failure does not affect others, and consistent voltage across components.
How do you calculate total resistance in a parallel circuit?
The total resistance (R_total) can be calculated using the formula: 1/R_total = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + ...
Can I use different types of components in a parallel circuit?
Yes, you can mix different types of components as long as they are compatible with the circuit voltage and current ratings.
What happens if one component fails in a parallel circuit?
If one component fails, the remaining components continue to function properly, as they have separate paths for current.
Are parallel circuits safe to use?
Yes, when designed correctly, parallel circuits are generally safe. However, care must be taken to avoid short circuits and overloads.
What are some common applications of parallel circuits?
Common applications include residential wiring, LED lighting systems, and battery configurations.
How do I test a parallel circuit?
You can test a parallel circuit using a multimeter to measure voltage and current at various points in the circuit.
Can I convert a series circuit to a parallel circuit?
Yes, but it requires careful reconfiguration of the connections to ensure proper voltage and current flow.
What tools do I need to build a parallel circuit?
You will need basic tools such as wire strippers, a soldering iron, a multimeter, and appropriate connectors.
Random Reads
- How to check graphics card memory windows 10
- How to clear thumbnail cache in windows
- How to create character skyrim
- How to create subscript
- How to create unique email
- Mastering command strips
- Mastering color blending in photoshop
- How to replace a bathroom sink
- How to transfer files from phone to pc or mac
- How to trace uk telephone number