Mastering the Art of Technical Specifications: A Comprehensive Guide
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Why Technical Specifications Matter
- Elements of a Technical Specification
- How to Write a Technical Specification
- Case Studies
- Best Practices for Writing Specifications
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Expert Insights
- FAQs
Introduction
Writing a technical specification can be daunting, yet it is a critical skill for engineers, developers, and project managers. A well-crafted technical specification serves as a blueprint for project stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is aligned and that the end product meets user needs and expectations.
Why Technical Specifications Matter
Technical specifications are essential for multiple reasons:
- Clarification: They clarify project requirements and expectations.
- Documentation: They provide a reference point for all stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
- Quality Assurance: They enable testing and validation of the final product against predefined criteria.
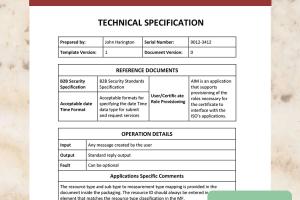
Elements of a Technical Specification
A comprehensive technical specification typically includes the following elements:
- Title: A clear and descriptive title.
- Purpose: An overview of the document's purpose and scope.
- Definitions: Clear definitions of key terms used.
- Requirements: Detailed functional and non-functional requirements.
- Assumptions: Any assumptions made during the specification process.
- Constraints: Limitations that affect the project.
- Acceptance Criteria: Criteria that must be met for the project to be considered complete.
- Appendices: Any additional information, such as diagrams or charts.
How to Write a Technical Specification
Writing a technical specification involves a systematic approach:
Step 1: Define the Purpose
Start by clearly defining the purpose of the specification. What problem does it aim to solve? Who are the intended users?
Step 2: Gather Requirements
Engage with stakeholders to gather detailed requirements. This may involve interviews, surveys, or workshops.
Step 3: Structure Your Document
Use the elements outlined above to create a structured document. Ensure each section flows logically into the next.
Step 4: Write Clear and Concise Content
Use straightforward language and avoid jargon. Use bullet points and tables for complex information.
Step 5: Review and Revise
Once the draft is complete, review it with stakeholders for feedback. Revise as necessary based on their inputs.
Step 6: Finalize and Distribute
Finalize the document and distribute it to all relevant parties. Ensure that it is accessible and stored in a shared location for future reference.
Case Studies
To illustrate the importance of technical specifications, let's look at a few case studies:
Case Study 1: Software Development
A software company faced issues with project delays due to vague requirements. After implementing a detailed technical specification process, they saw a 30% reduction in time-to-market.
Case Study 2: Product Design
A product design firm utilized technical specifications to align their multidisciplinary teams, resulting in a 50% decrease in design iterations and improved stakeholder satisfaction.
Best Practices for Writing Specifications
Here are some best practices to enhance your technical specification writing:
- Involve stakeholders early in the process.
- Use templates to maintain consistency.
- Regularly update specifications throughout the project lifecycle.
- Utilize visuals to support complex ideas.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When writing technical specifications, be aware of these common pitfalls:
- Being overly vague or generic.
- Failing to include acceptance criteria.
- Neglecting to revise documents based on stakeholder feedback.
Expert Insights
We reached out to industry experts for their thoughts on writing technical specifications:
"A well-defined specification can save teams from miscommunication and project delays." - Jane Doe, Project Manager
"Always keep your audience in mind. A specification should be understandable to all stakeholders." - John Smith, Technical Writer
FAQs
1. What is a technical specification?
A technical specification is a detailed document that outlines the requirements, features, and functionalities of a project or product.
2. Why are technical specifications important?
They provide clarity, serve as a reference document, and help ensure that the final product meets user needs.
3. How long should a technical specification be?
The length can vary greatly depending on the project, but it should be as long as necessary to convey all required information clearly.
4. Who should write a technical specification?
Typically, a technical writer or project manager will write the specification, often with input from engineers and other stakeholders.
5. How do I ensure my technical specification is clear?
Use simple language, avoid jargon, and include visual aids where appropriate to enhance understanding.
6. Can I use templates for technical specifications?
Yes, using templates can help maintain consistency and ensure that all necessary elements are included.
7. How often should I update my technical specification?
Specifications should be updated regularly, especially when project requirements change or new information becomes available.
8. What are the key components of a technical specification?
Key components include the title, purpose, definitions, requirements, assumptions, constraints, and acceptance criteria.
9. How do I gather requirements for a technical specification?
Engage stakeholders through interviews, surveys, and collaborative workshops to gather a comprehensive list of requirements.
10. What's the difference between functional and non-functional requirements?
Functional requirements describe what the system should do, while non-functional requirements describe how the system should perform (e.g., security, performance).
Random Reads
- How to hide link html css
- How to hide a file in an image file
- Unlimited cash bounty nfs most wanted
- How to make a treehouse in minecraft
- How to transmit audio with laser pen
- How to transfer photos from iphone to pc
- Mirror hard drive windows
- Mastering your turntable guide
- How to remove bleach stains from carpet
- How to measure a screen door