How to Efficiently Restart Windows Explorer Without Rebooting Your Computer
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- What is Windows Explorer?
- Why Restart Windows Explorer?
- How to Restart Windows Explorer
- Step-by-Step Guide
- Common Issues and Solutions
- Case Studies
- Expert Insights
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Windows Explorer is a critical component of the Windows operating system, responsible for the graphical user interface that allows users to navigate files and folders. However, like any software, it can occasionally run into issues that can affect your computer's performance. Restarting Windows Explorer can resolve many of these problems without the need for a full system reboot. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various methods for restarting Windows Explorer, the reasons why you might need to do so, and practical tips to enhance your Windows experience.
What is Windows Explorer?
Windows Explorer, also known as File Explorer, is the file management application in Windows. It provides a user-friendly interface for accessing files, folders, and drives. Windows Explorer allows users to perform various tasks, such as copying, moving, and deleting files, as well as managing system settings and network locations.
Why Restart Windows Explorer?
There are several reasons you might need to restart Windows Explorer, including:
- Performance Issues: If Windows Explorer is running slowly or freezing, restarting it can restore normal function.
- UI Problems: Graphical glitches, unresponsive windows, or missing taskbar items may require a restart to fix.
- Changes Not Applying: Sometimes, changes made to settings or files do not reflect immediately and require a restart to take effect.
- Memory Leaks: Windows Explorer can sometimes consume too much memory, leading to performance degradation. Restarting it can free up resources.
How to Restart Windows Explorer
Restarting Windows Explorer can be accomplished in several ways. Below, we will outline the most effective methods.
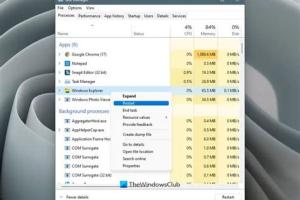
Method 1: Using Task Manager
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Locate Windows Explorer in the list of processes.
- Right-click on Windows Explorer and select Restart.
- Wait a few moments for the process to restart.
Method 2: Using Command Prompt
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type cmd and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
- Type the following commands one at a time, pressing Enter after each:
taskkill /f /im explorer.exestart explorer.exe
Method 3: Using PowerShell
- Press Win + X and select Windows PowerShell.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
Stop-Process -Name explorer -Force - Then, type:
Start-Process explorer
Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s delve deeper into each method with additional troubleshooting steps and tips to ensure a smooth experience.
Using Task Manager in Detail
When using Task Manager, ensure that you are viewing all processes. If you do not see Windows Explorer, click on More Details at the bottom of the Task Manager window. This will give you a complete view of all running processes.
Command Prompt Detailed Steps
The Command Prompt method is beneficial for users who prefer command-line interfaces. Make sure to run the Command Prompt as an administrator for the best results.
PowerShell Detailed Steps
PowerShell is a powerful tool that can also be used for more advanced troubleshooting. Ensure that you have the necessary permissions to execute scripts if needed.
Common Issues and Solutions
Even after restarting Windows Explorer, users may encounter problems. Here are some common issues and their solutions:
- Explorer Not Responding: If Windows Explorer fails to respond, try restarting it multiple times, or check for pending Windows updates that may resolve underlying issues.
- File Explorer Crashing: If the application crashes frequently, consider running a system file check through the Command Prompt with the command
sfc /scannow. - Taskbar Issues: If the taskbar is unresponsive after restarting Explorer, try restarting the computer or checking for malware that may be affecting system performance.
Case Studies
To better understand the effectiveness of restarting Windows Explorer, let’s look at a few real-world case studies:
Case Study 1: Performance Recovery
A user experienced significant lag while navigating through files. After restarting Windows Explorer via Task Manager, the performance returned to normal within minutes.
Case Study 2: UI Fix
Another user reported missing icons on their taskbar. Restarting Windows Explorer resolved the issue, restoring all missing icons without requiring a system reboot.
Expert Insights
Experts recommend regularly restarting Windows Explorer as part of system maintenance to prevent performance bottlenecks. Additionally, keeping the operating system updated can significantly reduce the frequency of issues requiring a restart.
Conclusion
Restarting Windows Explorer is a simple yet effective method to troubleshoot common issues without rebooting your computer. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can quickly restore functionality and improve your Windows experience. Regular maintenance and updates are key to keeping your system running smoothly.
FAQs
1. What happens if I restart Windows Explorer?
Restarting Windows Explorer refreshes the user interface and can fix issues like unresponsive windows or missing taskbar items.
2. Can restarting Windows Explorer cause data loss?
No, restarting Windows Explorer does not affect the data within your files; however, it's always a good idea to save your work before performing any system operation.
3. How often should I restart Windows Explorer?
There is no set frequency; however, if you notice performance issues or UI glitches, restarting it can be beneficial.
4. Is there a shortcut to restart Windows Explorer?
While there is no dedicated shortcut, using Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc) is the quickest way to restart it.
5. Will restarting Windows Explorer affect my open applications?
Restarting Windows Explorer will not close your open applications, but it may temporarily disrupt their visual elements.
6. What if Windows Explorer does not restart?
If it fails to restart, try using the Command Prompt or PowerShell methods outlined in this guide.
7. Can I restart Windows Explorer without Task Manager?
Yes, you can restart Windows Explorer using Command Prompt or PowerShell as detailed in this article.
8. Why does Windows Explorer keep crashing?
Frequent crashes can be due to corrupted files, software conflicts, or malware. Running system scans and keeping your OS updated can help.
9. Is restarting Windows Explorer safe?
Yes, it is completely safe and often recommended as a troubleshooting step for Windows performance issues.
10. How can I prevent issues with Windows Explorer?
Regularly update your operating system, run antivirus scans, and clear temporary files to help maintain optimal performance.