Mastering Antenna Construction: A Comprehensive Guide to Building Your Own Antennas
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding Antennas
- Types of Antennas
- Materials Needed
- Designing Your Antenna
- Step-by-Step Guide to Building Antennas
- Testing and Tuning Your Antenna
- Case Studies
- Expert Insights
- FAQs
Introduction
Building your own antennas can be a rewarding and cost-effective way to enhance your radio communication capabilities. Whether you're a hobbyist looking to explore the world of ham radio or a tech enthusiast aiming to improve your home network, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the entire process of understanding, designing, and constructing antennas. With step-by-step instructions and expert insights, you'll be able to master the art of antenna building.
Understanding Antennas
An antenna is a device that converts electrical energy into radio waves and vice versa. It is a crucial component in various communication systems, including televisions, radios, and mobile devices. Understanding how antennas work is fundamental to building an effective one.
The Science of Antennas
At its core, an antenna operates on the principles of electromagnetism. When an electrical signal passes through an antenna, it creates an electromagnetic field that can propagate through space. The efficiency of this process depends on various factors including:
- Frequency of operation
- Size and shape of the antenna
- Surrounding environment
- Impedance matching
Types of Antennas
There are numerous types of antennas, each designed for specific applications. Here are some of the most common types:
- Dipole Antennas: Simple and effective, ideal for general use.
- Yagi-Uda Antennas: Highly directional, perfect for TV reception.
- Log Periodic Antennas: Versatile and good for a wide range of frequencies.
- Loop Antennas: Compact and useful for shortwave communication.
- Monopole Antennas: Designed for vertical orientation, often used in mobile applications.
Materials Needed
Before diving into the construction of your antenna, gather the necessary materials:
- Copper or aluminum wire
- Insulators (plastic or ceramic)
- Soldering iron and solder
- Antenna tuner (if necessary)
- Coaxial cable
- Mounting hardware
Designing Your Antenna
The design of your antenna will significantly affect its performance. Consider the following factors:
- Operating frequency: Ensure your design is suitable for the frequencies you intend to use.
- Gain: Determine how much signal amplification you require.
- Radiation pattern: Decide on the directionality of your antenna.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building Antennas
Follow these steps to build a simple dipole antenna:
Step 1: Calculate the Length
Use the formula: Length (in feet) = 468 / Frequency (in MHz). For example, for a frequency of 144 MHz, the length would be 3.25 feet.
Step 2: Cut the Wire
Cut two equal lengths of wire based on your calculation. Each piece will serve as one arm of the dipole.
Step 3: Attach the Insulators
Securely tie insulators to both ends of each wire. These will help to keep the antenna stable and prevent short circuits.
Step 4: Connect the Coaxial Cable
Attach the coaxial cable to the center of the dipole. The center conductor connects to one wire, while the shield connects to the other.
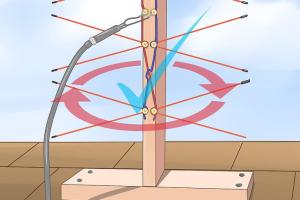
Step 5: Mount the Antenna
Use appropriate mounting hardware to elevate the antenna. Height can greatly influence performance.
Step 6: Test the Antenna
Use an SWR meter to test the Standing Wave Ratio. Adjust if necessary.
Testing and Tuning Your Antenna
After building your antenna, proper testing and tuning are crucial to ensure optimal performance. Follow these steps:
- Connect the antenna to your receiver or transmitter.
- Check the SWR to ensure it’s within an acceptable range (ideally under 1.5:1).
- Make adjustments to the length or configuration as needed.
Case Studies
Here are a few examples of successful antenna builds:
Case Study 1: The Backyard Ham Radio Setup
A radio enthusiast built a 40-meter dipole antenna in their backyard, achieving long-distance communication with minimal equipment.
Case Study 2: Portable Antenna for Camping
A portable Yagi antenna was designed specifically for camping trips, allowing users to maintain communication while off-grid.
Expert Insights
We spoke to several antenna experts who shared their tips for building effective antennas:
- Keep it Simple: Start with basic designs before moving to complex configurations.
- Experiment: Don’t hesitate to try different materials and designs.
- Document Your Work: Keep notes on what works and what doesn’t for future reference.
FAQs
1. What is the best material for building antennas?
Copper and aluminum are the most commonly used materials due to their excellent conductivity.
2. Can I build an antenna for TV reception?
Yes, many types of antennas, like Yagi-Uda antennas, are specifically designed for TV reception.
3. How do I know if my antenna is working properly?
Using an SWR meter is the best way to check the performance of your antenna.
4. What tools do I need to build an antenna?
You will need a soldering iron, wire cutters, and basic hand tools like pliers.
5. Is it legal to build my own antennas?
Yes, it is legal in most countries, but ensure you comply with local regulations.
6. How can I improve my antenna performance?
Height, placement, and proper tuning are key factors that affect antenna performance.
7. Can I use scrap materials to build an antenna?
Absolutely! Many builders use scrap metals and old electronics to create effective antennas.
8. What is a dipole antenna used for?
Dipole antennas are versatile and can be used for various communication applications, including ham radio.
9. How do I find the right frequency for my antenna?
Determine the frequencies you wish to operate on and design your antenna accordingly.
10. Where can I find more resources on antenna building?
There are many online forums, manuals, and videos dedicated to antenna construction.
Random Reads
- Easily install steam linux
- Easily download install ffmpeg windows pc
- How to download xbox 360 game
- How to download videos safely
- How to log out of yahoo mail
- How to login to a website as an admin
- How to change time synchronization interval windows
- Minecraft redstone dispenser loop
- How to get started in tekkit
- How to get started in warhammer