Mastering Your Windows PC: A Complete Guide to Changing BIOS Settings
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- What is BIOS?
- Why Change BIOS Settings?
- How to Access BIOS on Your Windows PC
- Common BIOS Settings
- Step-by-Step Guide to Change BIOS Settings
- Expert Tips for Optimizing BIOS Settings
- Troubleshooting BIOS Issues
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) is a crucial component of your computer's hardware that initializes the system's hardware before loading the operating system. Understanding how to change BIOS settings can help you optimize your computer's performance and troubleshoot various issues. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of changing BIOS settings on a Windows PC, from the basics to advanced configurations.
What is BIOS?
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System. It is firmware stored on a small memory chip on the motherboard of your computer. The BIOS is the first software that runs when you turn on your PC, and it prepares the system for booting the operating system. The BIOS controls the pathways between the operating system and the hardware components, including the hard drive, keyboard, and processor.
Key Functions of BIOS
- Power-on Self Test (POST): Checks the hardware components for errors.
- Booting: Identifies and initiates the boot device.
- Hardware Configuration: Manages settings for the CPU, RAM, and other peripherals.
- System Settings: Allows users to modify hardware settings for performance optimization.
Why Change BIOS Settings?
Changing BIOS settings can improve system performance, enable new hardware, or troubleshoot existing issues. Here are some reasons why you might want to access and modify your BIOS:
- Performance Optimization: Adjusting CPU clock speeds and RAM timings can enhance performance.
- Hardware Compatibility: Enabling or disabling features for newly installed hardware.
- Troubleshooting: Resetting BIOS to default settings can resolve boot issues.
- Security: Implementing a BIOS password can help secure your system from unauthorized access.
How to Access BIOS on Your Windows PC
Accessing the BIOS varies slightly between different manufacturers, but the general process is similar. Follow these steps:
1. Prepare Your Computer
Make sure your computer is off. If it is operating, restart it.
2. Identify the Right Key
During the startup process, you need to press a specific key to enter the BIOS setup. Common keys include:
- Del or F2 for most desktop computers.
- F10 for HP laptops.
- Esc for some Asus and Toshiba laptops.
3. Press the Key at Startup
As soon as the computer starts, repeatedly press the BIOS access key until you see the BIOS menu. If you miss the window, you may need to restart and try again.
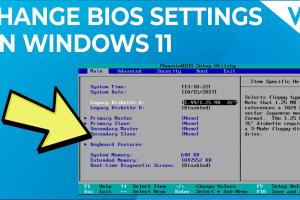
Common BIOS Settings
Within the BIOS setup, you will find several settings that you can adjust. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Boot Order: Determines the sequence of devices the computer boots from.
- CPU Configuration: Settings related to the processor, such as clock speed and virtualization support.
- RAM Settings: Configurations for memory speed and timings.
- Integrated Peripherals: Options to enable or disable built-in hardware like audio or network adapters.
Step-by-Step Guide to Change BIOS Settings
Changing BIOS settings can seem daunting, but following these steps will simplify the process:
Step 1: Enter BIOS Setup
Follow the instructions in the previous section to access the BIOS setup.
Step 2: Navigate the BIOS Menu
Use the arrow keys to navigate through the BIOS menu. The layout may vary by manufacturer, but the options are generally similar.
Step 3: Change Desired Settings
Highlight the setting you wish to change and press Enter. Use the arrow keys to select the desired option, and press Enter again to confirm.
Step 4: Save Changes and Exit
Once you have made your changes, navigate to the "Save & Exit" option, usually located at the top or bottom of the menu. Confirm any prompts to save your settings.
Expert Tips for Optimizing BIOS Settings
To get the most out of your BIOS settings, consider the following expert tips:
- Backup Your Settings: Before making changes, note your current settings in case you need to revert.
- Research Hardware Compatibility: Verify that your hardware supports any settings you wish to change, especially overclocking.
- Update BIOS Firmware: Check for firmware updates from your manufacturer to improve performance and compatibility.
Troubleshooting BIOS Issues
If you encounter issues after changing BIOS settings, here are some troubleshooting steps:
- Reset to Default: Return to the BIOS menu and select the "Load Default Settings" option.
- Check Connections: Ensure that all hardware components are properly connected.
- Clear CMOS: If problems persist, consider clearing the CMOS battery to reset BIOS settings.
Conclusion
Changing BIOS settings on a Windows PC can significantly impact your system's performance and functionality. By following this guide, you can confidently navigate your BIOS, make informed changes, and troubleshoot any issues that arise. Remember to approach BIOS modifications cautiously and always back up your settings for safekeeping.
FAQs
1. What is BIOS and why is it important?
BIOS is firmware that initializes hardware during the boot process, allowing the operating system to load. It is essential for system functionality.
2. How do I access BIOS on my Windows PC?
Restart your computer and press the designated key (like F2 or Del) during startup to enter the BIOS setup.
3. Can I change BIOS settings without affecting my system?
Yes, but be cautious. Incorrect settings can lead to system instability. It's best to note your original settings before making changes.
4. What are some common BIOS settings I should know about?
Common settings include boot order, CPU configuration, RAM settings, and integrated peripherals.
5. How do I reset BIOS settings to default?
Access BIOS setup, navigate to the "Load Default Settings" option, and confirm to reset.
6. What should I do if my computer won’t boot after changing BIOS settings?
Try entering BIOS again and resetting to default settings. Check hardware connections as well.
7. Is it safe to update BIOS firmware?
Yes, updating BIOS firmware can improve performance and stability, but it should be done carefully and with caution.
8. What does overclocking mean in BIOS?
Overclocking is the practice of increasing CPU and RAM speeds beyond the manufacturer's specifications for enhanced performance.
9. Can I add a BIOS password for security?
Yes, you can set a BIOS password to prevent unauthorized access to BIOS settings.
10. Where can I find more information on my specific BIOS version?
Check the manufacturer's website for documentation and resources related to your specific BIOS version.
Random Reads
- How to protect electronics from electromagnetic pulse
- Unlock whirlpool washer
- How to save flash animation from website
- How to log out of google play
- How to log out of hotmail
- How to test a transformer
- How to test a silicon diode with a multimeter
- Unzip files android files google
- Unzip files guide
- Unsync google photos