Mastering the Conversion: A Complete Guide to Converting Watts to Amps
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding the Basics
- The Formula for Conversion
- Exploring Voltage and Current
- Step-by-Step Guide to Converting Watts to Amps
- Examples and Case Studies
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Expert Insights
- FAQs
Introduction
Understanding how to convert watts to amps is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems. Whether you are an electrician, an engineer, or simply a DIY enthusiast, knowing how to perform this conversion can help ensure that your projects are both safe and efficient. In this extensive guide, we will explore the relationships between watts, amps, and volts, delve into the formulas needed for conversion, and provide examples and case studies to solidify your understanding.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into conversions, it's essential to grasp the fundamental concepts of electrical power, current, and voltage. Here's a brief overview:
- Watts (W): The unit of power representing the rate of energy transfer.
- Amps (A): The unit of electric current, indicating the flow of electric charge.
- Volts (V): The unit of electric potential, representing the difference in electric potential energy.
The relationship among these units can be expressed through a simple equation:
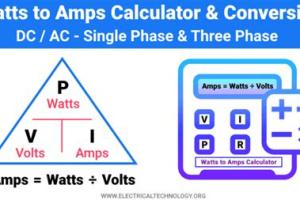
Power (W) = Current (A) × Voltage (V)
The Formula for Conversion
To convert watts to amps, you can rearrange the formula above:
Current (A) = Power (W) / Voltage (V)
This formula indicates that to find the current in amps, you need to divide the power in watts by the voltage in volts.
Exploring Voltage and Current
Voltage levels vary depending on the country and application. Common voltage levels include:
- 120V (common in household appliances in North America)
- 230V (common in Europe and other regions)
- 12V (common in automotive and low-voltage applications)
Understanding the voltage level is crucial for accurate conversions, as it directly affects the calculation of current.
Step-by-Step Guide to Converting Watts to Amps
Follow these steps to convert watts to amps:
- Identify the power in watts (W).
- Determine the voltage in volts (V).
- Apply the formula: Current (A) = Power (W) / Voltage (V).
- Perform the calculation to find the current in amps.
Examples and Case Studies
Let's explore some real-world examples to illustrate the conversion process:
Example 1: Household Appliance
A microwave oven has a power rating of 1000 watts and operates at 120 volts. To find the current:
Current (A) = 1000 W / 120 V = 8.33 A
Example 2: Electric Car Charger
An electric car charger rated at 2400 watts operating at 240 volts:
Current (A) = 2400 W / 240 V = 10 A
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While converting watts to amps, be mindful of these common pitfalls:
- Forgetting to use the correct voltage.
- Assuming all devices operate at the same voltage.
- Not accounting for power factor in AC circuits.
Expert Insights
Electrical engineering experts emphasize the importance of accurate calculations to prevent potential hazards. Here are some tips:
- Always double-check your voltage source.
- Use a multimeter for precise measurements.
- Understand the load requirements of your devices.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between watts and amps?
Watts measure power, while amps measure the flow of electric current. Watts = Amps × Volts.
2. How do I convert 500 watts to amps?
Assuming a voltage of 120V, the current would be 4.17 A (500 W / 120 V).
3. Do all devices use the same voltage?
No, voltage levels vary by region and device type. It's crucial to know the correct voltage for accurate conversions.
4. What is power factor?
Power factor is a measure of how effectively electrical power is being converted into useful work output. It is particularly important in AC circuits.
5. Can I use the same formula for AC and DC?
Yes, but for AC circuits, it's essential to consider the power factor.
6. What is the formula for converting amps to watts?
Power (W) = Current (A) × Voltage (V).
7. Why is knowing amps important for safety?
Understanding amps helps prevent overheating and potential electrical fires by ensuring that circuits are not overloaded.
8. Can I convert watts to amps without knowing voltage?
No, voltage is necessary to perform the conversion accurately.
9. Are there online calculators for this conversion?
Yes, many websites offer online calculators for converting watts to amps easily.
10. What should I do if I'm unsure about my calculations?
Consult an electrician or use a multimeter to verify your readings and calculations.
Random Reads
- How to find your way home in minecraft
- How to play candy crush saga
- How to play bakugan
- How to play among us
- 10 tips to drill through metal
- How to calculate total resistance in circuits
- Create borders in word
- Create calendar excel
- How to move heavy furniture upstairs
- How to tame and ride a horse in minecraft