Unlocking the Secrets: How to Hear Through Walls Effectively
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding Sound and Its Properties
- How Sound Travels Through Different Materials
- Listening Techniques and Tools
- Advanced Methods to Enhance Listening
- Case Studies and Real-World Applications
- Expert Insights on Acoustic Engineering
- Safety and Ethical Considerations
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
In a world filled with noise, the ability to hear through walls may seem like an intriguing superpower. Whether for safety, curiosity, or practical reasons, understanding how sound travels and how to amplify it can be beneficial. This comprehensive guide will explore the science behind sound, effective techniques for listening through walls, and ethical considerations surrounding this practice.
Understanding Sound and Its Properties
Sound is a form of energy that travels in waves through various mediums. To comprehend how to hear through walls, it's essential to understand the fundamental properties of sound.
What is Sound?
Sound is produced by vibrating objects. These vibrations disturb the surrounding air, creating sound waves that travel to our ears. Key properties of sound include:
- Frequency: Determines the pitch of the sound.
- Amplitude: Affects the volume of the sound.
- Wavelength: The distance between successive peaks of sound waves.
Types of Sound Waves
There are two main types of sound waves to consider:
- Longitudinal Waves: These waves compress and expand the medium through which they travel, such as air.
- Transverse Waves: These waves move perpendicular to the direction of the wave, often seen in water waves.
How Sound Travels Through Different Materials
The ability to hear through walls is influenced by the material's density and thickness. Understanding how sound interacts with different surfaces is crucial.
Factors Affecting Sound Transmission
- Material Type: Hard surfaces like concrete transmit sound differently than soft materials like drywall.
- Thickness: Thicker walls generally block sound more effectively.
- Surface Texture: Smooth surfaces can reflect sound waves, while textured ones may absorb them.
Soundproofing Techniques
While this guide focuses on hearing through walls, it's essential to recognize how soundproofing can inhibit this ability. Common soundproofing methods include:
- Acoustic panels
- Soundproof drywall
- Insulation materials
Listening Techniques and Tools
For those eager to hear what lies beyond their walls, various techniques and tools can enhance your listening capabilities.
Basic Techniques
Before investing in specialized equipment, consider these basic techniques:
- Placement: Position yourself close to the wall.
- Listening Posture: Lean your ear against the wall for better clarity.
- Silence: Minimize background noise to improve your hearing.
Tools for Enhanced Listening
For a more advanced approach, consider the following tools:
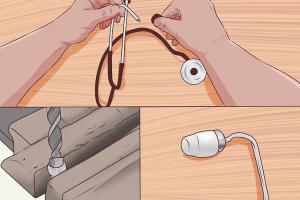
- Stethoscope: A medical stethoscope can amplify sounds transmitted through walls.
- Parabolic Microphone: This device captures sound from a distance and can be aimed towards the wall.
- Vibration Sensors: These can detect sound vibrations and convert them into audible sounds.
Advanced Methods to Enhance Listening
For those who are serious about hearing through walls, advanced techniques can yield better results.
Using Technology
Modern technology offers several solutions:
- Audio Amplifiers: Devices that enhance sound signals can be placed on the wall to pick up vibrations.
- Smartphone Apps: Some apps can analyze sounds and provide insights into what might be occurring on the other side.
DIY Listening Devices
If you're inclined to build your own devices, consider this simple DIY project:
- Gather materials like a microphone, amplifier, and headphones.
- Connect the microphone to the amplifier.
- Place the microphone against the wall and listen through the headphones.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Hearing through walls has practical applications, ranging from security to communication. Here are some real-world scenarios:
Case Study 1: Home Security
In urban settings, homeowners use listening devices to monitor suspicious activities outside their residences.
Case Study 2: Emergency Services
Firefighters and rescue teams often utilize advanced listening equipment to locate trapped individuals in collapsed structures.
Expert Insights on Acoustic Engineering
We consulted acoustic engineers to gather insights on effective techniques for hearing through walls. Here are some highlights:
Insight 1: The Importance of Frequency
Experts emphasize that lower frequencies travel better through walls than higher frequencies. This means that bass sounds are more likely to be heard.
Insight 2: The Role of Wall Composition
Understanding the composition of walls can aid in developing better listening strategies. For instance, wooden walls may transmit sound differently than brick walls.
Safety and Ethical Considerations
While the desire to hear through walls may stem from curiosity, it is essential to consider the ethical implications:
- Privacy: Respecting others' privacy is paramount.
- Legal Issues: Eavesdropping can have legal ramifications.
Conclusion
Hearing through walls is a fascinating blend of science and technique. By understanding sound properties, employing various listening techniques, and utilizing advanced tools, you can enhance your ability to listen effectively. However, always remember to respect privacy and legal boundaries.
FAQs
- Can I really hear through walls? Yes, sound can travel through walls, especially if the walls are thin or made of certain materials.
- What materials block sound best? Dense materials like concrete and brick are effective at blocking sound.
- Are there legal issues with listening through walls? Yes, eavesdropping can violate privacy laws depending on your location.
- What tools can I use to hear through walls? Stethoscopes, parabolic microphones, and specialized listening devices can enhance your ability to hear through walls.
- How does sound travel through walls? Sound travels through wall materials via vibrations, with different materials affecting sound transmission differently.
- Can I make my own listening device? Yes, simple devices can be constructed using microphones and amplifiers.
- Does sound travel better in certain frequencies? Yes, lower frequencies travel better through barriers than higher frequencies.
- What are the ethical considerations? Always respect privacy and be aware of local laws regarding eavesdropping.
- Is it safe to use listening devices? Using devices responsibly and legally is crucial to ensure safety.
- How can I improve my listening skills? Practicing active listening and minimizing background noise can help improve your ability to hear.
Random Reads
- How to unlock baby luigi mario kart wii
- How to unlock an oven
- Mastering rawlplugs
- Mastering powerpoint handouts
- Mastering image resizing
- Mastering image flipping
- Unlock national pokedex pokemon platinum
- How to use imac as external monitor
- How to use imessage
- How to watch videos from your phone on your tv