Understanding How to Calculate Adverse Impact: A Comprehensive Guide
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- What is Adverse Impact?
- Why is Adverse Impact Important?
- Legal Framework
- How to Calculate Adverse Impact
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculation
- Case Studies
- Common Misconceptions
- Expert Insights
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
In today's competitive job market, ensuring fair and equitable hiring practices is more important than ever. Adverse impact analysis is a crucial tool for organizations seeking to maintain compliance with equal employment opportunity laws and to promote diversity within their workforce. In this article, we will explore how to calculate adverse impact, its implications, and why it matters in the realm of human resources and employment law.
What is Adverse Impact?
Adverse impact refers to a situation in which a seemingly neutral employment practice disproportionately affects members of a protected group. This can occur in various stages of employment, including hiring, promotions, and terminations. Understanding adverse impact is vital for organizations to ensure they are not unintentionally discriminating against certain demographic groups.
Key Definitions
- Protected Groups: Categories of individuals protected by law from discrimination based on characteristics such as race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
- Disparate Impact: Another term often used interchangeably with adverse impact, referring to practices that may not appear discriminatory but result in unequal treatment.
Why is Adverse Impact Important?
Understanding and calculating adverse impact is crucial for several reasons:
- Compliance: Organizations can avoid legal repercussions by ensuring their hiring practices do not adversely affect protected groups.
- Diversity and Inclusion: By identifying adverse impact, companies can take proactive measures to foster a diverse and inclusive workplace.
- Reputation Management: Negative publicity surrounding discriminatory practices can harm an organization’s reputation and lead to a loss of business.
Legal Framework
The concept of adverse impact is rooted in federal laws such as Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which prohibits employment discrimination. Understanding these legal frameworks is essential for HR professionals and organizational leaders to navigate potential pitfalls in their hiring processes.
Relevant Legislation
- Title VII of the Civil Rights Act (1964): Prohibits employment discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
- Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC): Enforces federal laws against employment discrimination.
- Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA): Protects workers aged 40 and older from discrimination.
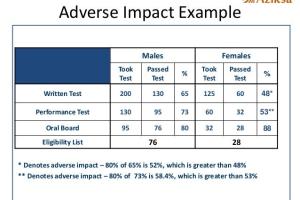
How to Calculate Adverse Impact
The calculation of adverse impact typically involves statistical analysis to compare selection rates among different demographic groups. The four-fifths rule is a common method used to determine whether adverse impact exists.
Four-Fifths Rule
The four-fifths rule states that if the selection rate for any protected group is less than four-fifths (or 80%) of the selection rate for the group with the highest rate, then adverse impact may be present.
Basic Formula
The basic formula for calculating adverse impact is:
Adverse Impact Ratio = (Selection Rate of Protected Group) / (Selection Rate of Non-Protected Group)Step-by-Step Guide to Calculation
To accurately calculate adverse impact, follow these steps:
- Identify Groups: Determine the demographic groups involved in the analysis (e.g., gender, ethnicity).
- Collect Data: Gather data on the selection rates of each group for the specific employment decision (e.g., hiring, promotions).
- Calculate Selection Rates: Calculate the selection rate for each group by dividing the number of people selected by the total number of applicants in that group.
- Apply the Four-Fifths Rule: Compare the selection rates and apply the four-fifths rule to determine if adverse impact exists.
- Document Findings: Keep records of your calculations and findings for compliance and analysis.
Case Studies
Analyzing real-world examples of adverse impact can provide valuable insights into how organizations can effectively address these issues.
Case Study 1: XYZ Corporation
XYZ Corporation, a large tech firm, faced scrutiny after an internal audit revealed that their hiring process for software engineers resulted in a 65% selection rate for female candidates compared to 85% for male candidates. This discrepancy prompted an adverse impact analysis which led to the revision of their selection criteria.
Case Study 2: ABC Healthcare
ABC Healthcare conducted an adverse impact analysis during their hiring process for nursing positions. The analysis revealed that minority applicants were selected at a rate of 70% compared to 90% for non-minority applicants, indicating potential discrimination. They implemented targeted outreach programs to improve diversity in their applicant pool.
Common Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions surrounding adverse impact that can hinder effective analysis:
Misconception 1: Adverse Impact Equals Intentional Discrimination
Many believe that adverse impact implies intentional discrimination; however, it can occur even in well-meaning organizations.
Misconception 2: All Disparities Constitute Adverse Impact
Not all disparities indicate adverse impact. Statistical significance must be determined through rigorous analysis.
Expert Insights
Experts in human resources and employment law emphasize the importance of proactive measures in preventing adverse impact. Regular audits, diversity training, and transparent hiring practices are key strategies to foster an equitable workplace.
Conclusion
Calculating adverse impact is essential for organizations committed to fair hiring practices and compliance with employment laws. By understanding the implications and employing effective analysis methods, companies can make strides towards a more inclusive workforce.
FAQs
1. What is adverse impact in hiring?
Adverse impact refers to a hiring practice that disproportionately affects a specific demographic group negatively.
2. How is adverse impact calculated?
It is typically calculated using the four-fifths rule, comparing selection rates among different demographic groups.
3. Why is it important to analyze adverse impact?
It helps organizations ensure compliance with employment laws and promote diversity and inclusion.
4. What are protected groups?
Protected groups are categories of individuals protected by law from discrimination, such as race, gender, or religion.
5. Can adverse impact occur unintentionally?
Yes, adverse impact can occur even with neutral hiring practices if those practices disproportionately affect a protected group.
6. How can organizations mitigate adverse impact?
Implementing targeted outreach, revising selection criteria, and conducting regular audits can help mitigate adverse impact.
7. What is the four-fifths rule?
The four-fifths rule states that if the selection rate for any protected group is less than 80% of the highest rate, adverse impact may be present.
8. Is adverse impact analysis required by law?
While not explicitly required, it is strongly recommended for compliance with equal employment opportunity regulations.
9. What should organizations do after identifying adverse impact?
Organizations should document their findings and take corrective action to address the identified disparities.
10. Are there resources for further information on adverse impact?
Yes, the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) provides guidelines and resources for understanding and analyzing adverse impact.
Random Reads
- How to get lugia soul silver
- How to run software directly off usb flash drive
- How to run linux from usb
- How to choose vinyl plank flooring
- How to choose smartphone
- Mastering the art of adding download links
- Easy ways to type in a web address
- How to uninstall minecraft
- How to uninstall opera
- Ultimate guide jailbreaking ps3