Mastering Voltage Calculation: A Comprehensive Guide to Determining Voltage Across a Resistor
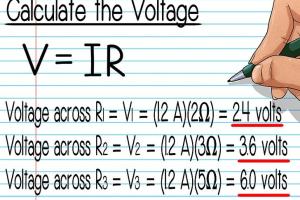
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding Voltage
- Ohm's Law Explained
- Resistors and Their Role in Circuits
- How to Calculate Voltage Across a Resistor
- Step-by-Step Guide to Voltage Calculation
- Practical Examples and Case Studies
- Common Mistakes in Voltage Calculation
- Expert Insights on Voltage Measurement
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Introduction
Understanding how to calculate voltage across a resistor is fundamental in electrical engineering and electronics. Voltage, measured in volts (V), represents the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. This guide will delve into the intricacies of voltage calculation, providing you with a robust understanding of the principles involved and practical applications.
Understanding Voltage
Voltage is a crucial concept in the world of electricity. It's what drives current through a circuit. To grasp voltage fully, we need to explore its relationship with current and resistance, which is encapsulated in Ohm's Law.
Ohm's Law Explained
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electronics that states:
V = I × R
- V = Voltage (Volts)
- I = Current (Amperes)
- R = Resistance (Ohms)
This equation allows us to calculate the voltage across a resistor when we know the current flowing through it and its resistance. It forms the backbone of electrical circuit analysis.
Resistors and Their Role in Circuits
Resistors are passive components that limit the flow of electrical current in a circuit. They are essential for controlling voltage and current levels and are used in various applications, from simple circuits to complex electronics.
When current passes through a resistor, a voltage drop occurs across it. This drop can be calculated using Ohm's Law, making resistors pivotal in managing circuit behavior.
How to Calculate Voltage Across a Resistor
To calculate the voltage across a resistor, follow these steps:
- Identify the current (I) flowing through the resistor.
- Determine the resistance (R) of the resistor.
- Use Ohm's Law to calculate the voltage (V) using the formula V = I × R.
Step-by-Step Guide to Voltage Calculation
Let’s break down the calculation process into detailed steps:
Step 1: Measure Current
Use an ammeter to measure the current flowing through the circuit. Ensure your meter is set to the correct range to avoid damaging the device.
Step 2: Find Resistance
Find the resistance value of the resistor. This information is generally marked on the resistor or can be found in the circuit diagram.
Step 3: Apply Ohm's Law
Once you have both values, simply multiply them:
V = I × R
For example, if the current is 2A and the resistance is 5Ω, the voltage across the resistor would be:
V = 2A × 5Ω = 10V
Practical Examples and Case Studies
Let’s consider a few practical scenarios to illustrate the calculation of voltage across a resistor:
Example 1: Simple Circuit
In a basic circuit with a 10Ω resistor and a current of 3A, the voltage can be calculated as:
V = 3A × 10Ω = 30V
Example 2: Series Circuit
In a series circuit with two resistors (10Ω and 20Ω) and a total current of 1A, the voltage across each can be calculated individually:
- For 10Ω: V = 1A × 10Ω = 10V
- For 20Ω: V = 1A × 20Ω = 20V
Example 3: Parallel Circuit
In a parallel circuit where two resistors (5Ω and 10Ω) share a total current of 2A, we can find the voltage across each resistor:
- For 5Ω: V = 2A × 5Ω = 10V
- For 10Ω: V = 2A × 10Ω = 20V
Common Mistakes in Voltage Calculation
When calculating voltage across a resistor, avoid these common pitfalls:
- Using incorrect units (e.g., mixing ohms and kilo-ohms).
- Failing to measure current correctly, leading to inaccurate voltage calculations.
- Neglecting the impact of other circuit elements when working with complex circuits.
Expert Insights on Voltage Measurement
Industry experts recommend utilizing digital multimeters for accurate voltage readings. Additionally, always ensure that your circuit is powered down before making any connections to avoid damaging your equipment or injuring yourself.
FAQs
1. What is voltage?
Voltage is the electric potential difference between two points in a circuit.
2. How do you measure voltage across a resistor?
Use a voltmeter connected in parallel with the resistor to measure the voltage drop.
3. Can you calculate voltage without knowing current?
No, you need either the current flowing through the resistor or the total circuit voltage to calculate voltage across it.
4. What happens if you have too much voltage across a resistor?
Excess voltage can lead to overheating and potentially damaging the resistor.
5. Is it safe to measure voltage in a live circuit?
While it can be done, it requires caution and proper equipment to ensure safety.
6. What is the unit for measuring voltage?
Voltage is measured in volts (V).
7. How can I calculate voltage drop in a series circuit?
Use Ohm's Law: V = I × R for each resistor in the series.
8. What is the difference between series and parallel voltage calculations?
In series, voltage adds up across components; in parallel, the voltage across each component is the same.
9. Can I use resistors in series and parallel together?
Yes, but you need to calculate equivalent resistance for accurate voltage calculations.
10. Where can I find more resources on electrical calculations?
Refer to educational websites like Electrical4U or Electronics Tutorials for more information.
Conclusion
Calculating voltage across a resistor is a vital skill in electronics. By mastering the principles of Ohm's Law and practicing with real-world examples, you can enhance your understanding and application of electrical concepts. Whether you're a student, hobbyist, or professional, the ability to accurately measure and calculate voltage will serve you well in your journey through the world of electronics.
Random Reads
- Increase microphone volume android
- Improve search engine optimization
- How to switch from hotmail to gmail
- How to sweep a floor expert tips
- How to reset a ps3
- How to reset a dell laptop
- How to rotate google photos android
- How to rotate computer screen
- Mastering http post requests in android
- Mastering header rows excel