Mastering File Copying in Linux: The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding Linux File Systems
- Basic File Copying Commands
- Advanced File Copying Techniques
- Copying Files with GUI Tools
- Case Studies
- Best Practices for File Copying
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Linux is a powerful operating system used by millions worldwide. Copying files is one of the most fundamental tasks that users perform. Whether you're a seasoned developer or a beginner, understanding how to copy files effectively can enhance your productivity. This guide will cover everything you need to know about copying files in Linux, including command-line tools, graphical interfaces, best practices, and troubleshooting tips.
Understanding Linux File Systems
Before diving into file copying, it’s essential to understand the Linux file system structure. Linux organizes files in a hierarchical format, starting from the root directory (/). Familiarity with this structure will help you navigate easily and locate files to copy.
- /home - Contains user home directories.
- /etc - Configuration files for the system.
- /var - Variable data files like logs.
- /tmp - Temporary files.
Basic File Copying Commands
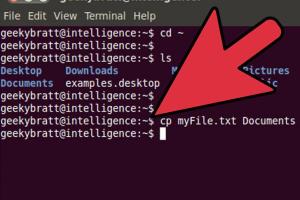
The most common command for copying files in Linux is the cp command. Below are some basic usages of the cp command.
1. Copying Files
cp source_file destination_fileThis command copies source_file to destination_file. If destination_file exists, it will be overwritten without warning.
2. Copying Directories
To copy directories, use the -r (recursive) option:
cp -r source_directory destination_directory3. Copying with Options
- -i: Prompts before overwriting files.
- -u: Copies files only if the source is newer than the destination.
- -v: Verbose mode, shows what is being copied.
Example command:
cp -iv source_file destination_fileAdvanced File Copying Techniques
While the basic cp command covers most scenarios, there are advanced techniques that can be beneficial.
1. Using rsync for Efficient Copying
The rsync command is a powerful tool for copying files and directories. It is particularly efficient for large files or when transferring over the network.
rsync -avz source_directory/ destination_directory/2. Copying Files Over SSH
To copy files securely over SSH, you can use:
scp local_file user@remote_host:/path/to/destination3. Using Tar for Archiving
When you need to copy a directory and its contents, using tar can be efficient:
tar -cvf archive.tar directory_to_copyCopying Files with GUI Tools
Many Linux distributions come with graphical user interfaces (GUIs) that simplify file management. Tools like Nautilus (Gnome Files) or Dolphin (KDE) allow users to drag and drop files easily.
1. Using Nautilus
In Nautilus, simply navigate to your file, right-click, select Copy, navigate to the destination, and select Paste.
Case Studies
To illustrate the effectiveness of these commands, we’ll explore a few real-world scenarios.
1. Backup Strategy for Personal Use
Consider a user who wants to back up their documents. They can create a script using rsync to automate this task daily:
rsync -av --delete /home/user/Documents/ /backup/Documents/2. Development Environment Setup
A developer might need to copy project files between environments. Using scp for secure copying can ensure files are transferred without exposure:
scp -r /local/project user@remote:/var/www/projectBest Practices for File Copying
To ensure efficiency and safety when copying files, consider these best practices:
- Always check your commands with
--dry-runoption where applicable. - Use version control for important projects.
- Regularly back up data to prevent loss.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even experienced users encounter issues. Here are some common problems and solutions:
- Permission Denied: Use
sudoto gain elevated permissions. - File Not Found: Double-check your file paths and names.
- Disk Space Issues: Ensure there’s enough space on the destination drive.
Conclusion
Copying files in Linux is a fundamental skill that can significantly enhance your workflow. With the knowledge of various commands and tools, you can efficiently manage your file copying tasks. Whether you prefer the command line or GUI, mastering these techniques will make you a more proficient Linux user.
FAQs
1. What is the cp command in Linux?
The cp command is used to copy files and directories in Linux.
2. Can I copy files over a network?
Yes, you can use commands like scp and rsync to copy files over a network.
3. How do I copy a directory in Linux?
Use the cp command with the -r option: cp -r source_directory destination_directory.
4. What does the -i option do in cp?
The -i option prompts the user before overwriting an existing file.
5. How can I copy files securely?
Use the scp command for secure copying over SSH.
6. What is rsync?
rsync is a utility for efficiently transferring and synchronizing files between a local and a remote system.
7. How do I copy files from one user to another?
Ensure you have the proper permissions and use the cp or rsync commands accordingly.
8. Can I use wildcards with the cp command?
Yes, wildcards can be used to copy multiple files at once, e.g., cp *.txt destination/.
9. How do I check if my copy was successful?
You can use the ls command to verify the presence of the copied files in the destination directory.
10. What should I do if I accidentally overwrite a file?
Check if you have backups or use file recovery tools if necessary.