Mastering Microsoft Word: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Simple Tables
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding Tables in Word
- Creating a Simple Table
- Formatting Your Table
- Advanced Table Features
- Using Tables for Data Organization
- Case Studies
- Expert Insights
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- FAQs
Introduction
Creating tables in Microsoft Word can significantly enhance your document's organization and presentation. Whether you're preparing a report, a project proposal, or a simple list, tables help in structuring information clearly and concisely. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of creating simple tables in Microsoft Word, ensuring you master the necessary skills to elevate your document design.
Understanding Tables in Word
Before diving into the practical steps, it's essential to understand what tables are and how they function in Microsoft Word. A table is essentially a grid that allows you to organize data in rows and columns, making it easier for readers to understand complex information at a glance.
- Rows: Horizontal lines of data.
- Columns: Vertical lines of data.
- Cells: The intersection of a row and a column, where data is entered.
Creating a Simple Table
Follow these step-by-step instructions to create a simple table in Microsoft Word:
Step 1: Open Microsoft Word
Begin by launching Microsoft Word on your device. Open a new or existing document where you want to insert the table.
Step 2: Navigate to the Insert Tab
In the ribbon at the top of the screen, click on the Insert tab. This will reveal various options for inserting different elements into your document.
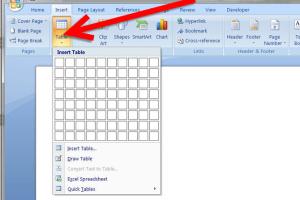
Step 3: Click on the Table Icon
In the Insert tab, locate the Table icon. Clicking it will open a dropdown menu with options for creating a table.
Step 4: Select Table Size
You can create a table by either dragging your mouse over the grid to select the number of rows and columns you want or by clicking on Insert Table for more precise control over the dimensions.
Step 5: Enter Your Data
Once the table appears in your document, click inside each cell to enter your data. You can navigate between cells using the Tab key.
Formatting Your Table
Formatting your table is crucial for enhancing its appearance and improving readability. Here’s how to format your table effectively:
Step 1: Select the Table
Click anywhere within the table to select it. You’ll notice a new set of tabs appear in the ribbon: Table Design and Layout.
Step 2: Apply Table Styles
Under the Table Design tab, you’ll find various pre-designed table styles. Hover over them to preview how they will look in your document, then click to apply your desired style.
Step 3: Adjust Cell Size
You can manually adjust the size of the rows and columns by dragging the borders. Additionally, if you want to make all cells the same size, select the entire table, then go to the Layout tab and click on Distribute Rows or Distribute Columns.
Step 4: Customize Borders and Shading
To further enhance your table, you can customize its borders and shading. In the Table Design tab, use the Borders dropdown to choose which borders to show or hide, and use the Shading option to fill cells with color.
Step 5: Text Alignment and Font Changes
Change the font style, size, and alignment of the text within cells using the options in the Home tab. You can center, left-align, or right-align text to match your document's design.
Advanced Table Features
Once you've mastered the basics, explore these advanced features to make your tables even more effective:
Merging and Splitting Cells
To merge cells, select the cells you want to combine, right-click, and choose Merge Cells. To split a cell, right-click on the cell and select Split Cells, then specify the number of rows and columns.
Using Formulas in Tables
Word allows you to perform calculations within tables. Click in the cell where you want the result, go to the Layout tab, and click on Formula. You can enter basic calculations using functions like SUM, AVERAGE, etc.
Inserting Images and Hyperlinks
You can enhance your tables by inserting images or hyperlinks. To add an image, click into a cell, navigate to the Insert tab, and select Pictures. For hyperlinks, right-click the text, choose Hyperlink, and enter the URL.
Using Tables for Data Organization
Tables can be powerful tools for organizing various types of data. Here are a few real-world applications:
Project Timelines
Use tables to create detailed timelines for projects, with columns for tasks, deadlines, and responsible parties.
Budget Tracking
Set up a budget table that tracks income and expenses, making it easy to visualize financial data.
Research Data
Organize research findings in a table format, allowing for quick comparisons between different data points.
Case Studies
Real-world examples can shed light on the practical applications of tables in Microsoft Word. Here are a few case studies:
Case Study 1: Corporate Training Program
A multinational corporation implemented tables in their training manuals, improving clarity and understanding among employees. As a result, training completion rates increased by 30%.
Case Study 2: Academic Research Paper
A university professor used tables to present complex statistical data in a paper, leading to higher engagement and citation rates from peers.
Expert Insights
Experts in document design and productivity emphasize the importance of tables in enhancing document readability. According to Dr. Jane Smith, a productivity expert, "Well-structured tables can transform a cluttered document into a reader-friendly format, making information accessible and actionable."
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Even seasoned users can encounter issues while working with tables in Word. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
Table Not Formatting Correctly
If your table doesn't appear as expected, ensure you've selected the correct table style and adjusted the cell sizes.
Data Overflowing Cells
To fix overflowing text, adjust the column width or use the text wrapping options in the Layout tab.
Difficulty Selecting Cells
If you find it hard to select specific cells, try using the table selection handle that appears in the top-left corner when you click inside the table.
FAQs
- Q1: Can I create a table in Word without using the mouse?
A1: Yes, you can use keyboard shortcuts like Alt + N, T to insert a table. - Q2: How do I resize a table quickly?
A2: Click and drag the table edges or adjust the width and height in the Layout tab. - Q3: Can I use tables in header or footer sections?
A3: Yes, you can insert tables into headers and footers just like you do in the main document. - Q4: How do I convert text to a table?
A4: Select the text you want to convert, navigate to the Insert tab, and choose Convert Text to Table. - Q5: Can I print a document with tables?
A5: Yes, tables will print as they appear in the document. - Q6: Is it possible to add a table from Excel?
A6: Yes, you can copy a table from Excel and paste it into Word. - Q7: How do I add borders to specific cells?
A7: Select the cells, go to the Table Design tab, and use the Borders dropdown to customize. - Q8: Can I change the direction of text in a cell?
A8: Yes, select the cell, right-click, and choose Text Direction to rotate the text. - Q9: How do I delete a table?
A9: Select the table and press Delete or right-click and choose Delete Table. - Q10: Are there keyboard shortcuts for table navigation?
A10: Yes, use Tab to move to the next cell and Shift + Tab to move to the previous cell.
Random Reads
- How to have infinite money in gta v
- Screenshot lenovo laptop
- Seamless contact transfer nokia phones
- How to make your own pokemon
- How to make your own custom pokemon card
- How to make a graph in microsoft word
- How to send files to iphone over bluetooth
- Mastering pet control sims 2
- Mastering parental controls
- How to organize a kitchen