Mastering CPU Overclocking: A Comprehensive Guide to Boosting Performance
-
Quick Links:
- 1. Introduction to CPU Overclocking
- 2. Understanding Your CPU
- 3. The Basics of Overclocking
- 4. Necessary Tools for Overclocking
- 5. Step-by-Step Guide to Overclocking a CPU
- 6. Monitoring and Testing Your Overclock
- 7. Cooling Solutions for Overclocking
- 8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 9. Conclusion
- 10. FAQs
1. Introduction to CPU Overclocking
Overclocking a CPU is the process of increasing its clock speed beyond the manufacturer's specifications. This can enhance performance, which is particularly beneficial for gaming, video editing, and other resource-intensive tasks. However, it comes with risks, including overheating and hardware damage if not done correctly.
2. Understanding Your CPU
The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is often referred to as the brain of your computer. It processes instructions and manages data flow in a computer system. Understanding your CPU's architecture, core count, and thermal design power (TDP) is crucial before attempting to overclock it.
2.1 Architecture
Most modern CPUs come with different architectures (like Intel's Core or AMD's Ryzen), which dictate their performance capabilities and how they can be overclocked.
2.2 Core Count
More cores can improve performance in multi-threaded applications, but overclocking will affect all cores, so knowing the core count helps set realistic expectations.
2.3 Thermal Design Power (TDP)
TDP indicates how much heat a CPU generates under maximum load. It’s vital to ensure that your cooling solution can handle the increased heat from overclocking.
3. The Basics of Overclocking
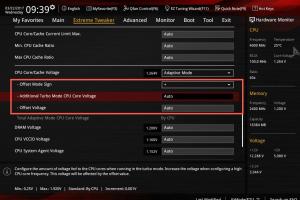
Overclocking involves adjusting the CPU multiplier and base clock settings in the BIOS/UEFI. Understanding voltage settings is also critical, as increasing voltage can lead to higher performance but also increases heat output.
3.1 CPU Multiplier
The CPU multiplier determines how fast the CPU processes instructions. Increasing the multiplier can lead to significant performance gains.
3.2 Base Clock (BCLK)
The base clock is the frequency that the CPU operates at. Adjusting this can impact not just the CPU but also other components, so it’s essential to proceed with caution.
3.3 Voltage Settings
Increased voltage can stabilize a CPU at higher speeds but also raises the risk of overheating. Balancing performance with safety is crucial.
4. Necessary Tools for Overclocking
- CPU-Z: A utility for monitoring CPU specifications and performance.
- HWMonitor: For tracking temperatures and voltages.
- Prime95: A stress-testing tool to test CPU stability.
- Core Temp: Monitors CPU temperature to ensure safe operation.
- BIOS/UEFI: The firmware interface where overclocking adjustments are made.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Overclocking a CPU
5.1 Preparation
- Ensure you have adequate cooling solutions in place.
- Update your motherboard BIOS to the latest version.
- Gather monitoring tools to keep track of temperatures and performance.
5.2 Entering BIOS/UEFI
Restart your computer and enter the BIOS/UEFI by pressing a designated key (often Delete, F2, or Esc) during boot-up.
5.3 Adjusting CPU Multiplier and Base Clock
- Locate the CPU settings in the BIOS.
- Increase the CPU multiplier by one increment.
- If desired, adjust the base clock to a safe level.
5.4 Voltage Adjustments
Increase the CPU core voltage (Vcore) gradually. Start with small increments (0.01V) to find a stable point.
5.5 Save and Exit BIOS
Save your changes and exit the BIOS. The system will reboot with the new settings.
5.6 Stress Testing
Use Prime95 or a similar tool to stress test your CPU for at least 30 minutes to ensure stability.
5.7 Monitor Temperatures
Use HWMonitor to check CPU temperatures during the stress test. If temperatures exceed safe limits (typically above 85°C), revert to previous settings.
6. Monitoring and Testing Your Overclock
It’s essential to continuously monitor your CPU performance and temperatures to ensure stability and safety. After overclocking, run various benchmarks to compare performance against your original settings.
6.1 Benchmarking Tools
- Cinebench: Renders images to test CPU performance.
- Geekbench: Provides a comprehensive performance score across multiple tasks.
- 3DMark: Tests gaming performance.
7. Cooling Solutions for Overclocking
Effective cooling is crucial when overclocking. Here are some cooling solutions to consider:
- Air Coolers: High-performance air coolers can dissipate heat effectively.
- Liquid Cooling: Offers superior cooling capabilities, especially for extreme overclocking.
- Thermal Paste: Ensure you apply high-quality thermal paste to improve heat transfer.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overvolting without monitoring temperatures.
- Skipping stress tests after making changes.
- Not having adequate cooling solutions in place.
- Rushing the process; take your time to find stable settings.
9. Conclusion
Overclocking can significantly improve your CPU's performance, but it requires careful planning, the right tools, and a willingness to experiment. Always keep safety in mind, make gradual adjustments, and monitor your results closely to find the sweet spot for your CPU.
10. FAQs
What is CPU overclocking?
CPU overclocking is the process of increasing a CPU’s clock speed beyond the manufacturer's specifications to enhance performance.
Is overclocking safe?
Overclocking can be safe if done correctly with proper cooling and monitoring, but it can also void warranties and risk hardware damage.
What tools do I need to overclock my CPU?
You will need monitoring tools like CPU-Z, HWMonitor, and stress testing software like Prime95.
Can all CPUs be overclocked?
No, only CPUs that have an unlocked multiplier (like Intel's K-series or AMD's Ryzen) can be easily overclocked.
How much can I overclock my CPU?
The amount you can overclock depends on your specific CPU model, cooling solutions, and motherboard capabilities.
What is the best cooling solution for overclocking?
Liquid cooling solutions generally provide the best thermal performance, but high-end air coolers can also be effective.
How do I know if my CPU is stable after overclocking?
Run stress tests for several hours and monitor temperatures. If the system crashes or temperatures exceed safe limits, revert to previous settings.
What are the risks of overclocking?
Risks include overheating, system instability, and potential hardware damage.
Can I overclock my laptop CPU?
Overclocking laptop CPUs is generally not recommended due to limited cooling capacity and higher risks of overheating.
Is overclocking worth it?
It can be worth it for users who require additional performance for gaming or demanding applications, but it requires care and caution.
Random Reads
- How to transmit audio with laser pen
- How to make your bedroom look cosy
- Mastering safe movie downloads utorrent
- Mastering sql files
- How to make your twitch stream private
- Linux set time zone
- Locate temp files
- How to turn on whatsapp notifications android
- How to increase disk space in vmware
- How to increase android volume