How to Easily Set Up a Wireless Hotspot on Windows Using Command Prompt
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding Wireless Hotspots
- Prerequisites for Setting Up a Hotspot
- Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up a Wireless Hotspot
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Case Studies
- Expert Insights
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
In today's digital age, having internet access is not just a luxury; it's a necessity. Sometimes, we find ourselves in situations where we need to share our internet connection with other devices. Whether it's for a gathering, a meeting, or simply for convenience, setting up a wireless hotspot on your Windows computer is a skill worth mastering. In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through the process of setting up a wireless hotspot using Command Prompt, ensuring that you can share your internet connection effortlessly.
Understanding Wireless Hotspots
A wireless hotspot is a physical location where people can access the internet via Wi-Fi, often using a router. However, did you know that your Windows device can act as a hotspot too? This allows multiple devices to connect and use your internet connection. Understanding the underlying technology will help you troubleshoot and optimize your hotspot setup.
What is a Wireless Hotspot?
A wireless hotspot is a device that enables internet access to users through a wireless network. It can be set up using dedicated hardware or software, allowing personal computers to share their internet connection.
Types of Hotspots
- Public Hotspots: Usually found in cafes and airports.
- Private Hotspots: Created by individuals to share their internet connection.
Prerequisites for Setting Up a Hotspot
Before diving into the setup process, ensure you have the following:
- A Windows Computer: This guide applies to Windows 10 and Windows 11.
- An Active Internet Connection: You need an internet connection to share.
- Administrator Access: You need admin rights to run Command Prompt commands.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up a Wireless Hotspot
Now that you're equipped with the basics and prerequisites, let's get started with the step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Open Command Prompt as Administrator
To begin, you need to open Command Prompt with administrative privileges:
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard.
- Type cmd in the search bar.
- Right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as administrator.
Step 2: Check Your Network Adapter
It’s important to know the name of your network adapter. Use the following command:
netsh wlan show drivers
Look for the line that says Hosted network supported. It should say Yes.
Step 3: Set Up the Hotspot
Now, you will set up the hotspot using a simple command:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=YourHotspotName key=YourPassword
Replace YourHotspotName with your desired name and YourPassword with a strong password.
Step 4: Start the Hotspot
To start the hotspot, enter the following command:
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
Your wireless hotspot is now active! You can connect your other devices using the SSID and password you set.
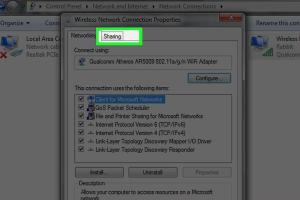
Step 5: Share Your Internet Connection
The last step is to share your internet connection with your new hotspot:
- Go to Control Panel.
- Select Network and Sharing Center.
- Click on Change adapter settings.
- Right-click on your internet connection and select Properties.
- Go to the Sharing tab.
- Check the box next to Allow other network users to connect through this computer's Internet connection.
- Select your hotspot connection from the dropdown menu.
- Click OK.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with a straightforward setup, issues may arise. Here are some common problems and solutions:
Hotspot Not Working
If your hotspot isn’t functioning, make sure:
- Your Wi-Fi driver is up to date.
- Hosted network is supported (as checked in Step 2).
- The hotspot is started using the command from Step 4.
Slow Internet Speed
If the internet speed is slow, consider the following:
- Limit the number of connected devices.
- Ensure your primary internet connection is stable.
Case Studies
Let’s explore a couple of real-world scenarios where users successfully set up wireless hotspots:
Case Study 1: Remote Work Setup
John, a freelance graphic designer, often works from cafes. By setting up a wireless hotspot on his laptop, he can continue to work seamlessly without being tied to a power outlet or single internet source.
Case Study 2: Family Gathering
During a family reunion, Sarah set up a wireless hotspot on her Windows laptop, allowing everyone to share the internet for streaming, gaming, and sharing photos without needing a separate router.
Expert Insights
According to networking experts, using a wireless hotspot is becoming increasingly popular, especially with the rise of remote work. Setting up a hotspot allows for greater flexibility and connectivity, making it an invaluable skill in the modern age.
Conclusion
Setting up a wireless hotspot on Windows using Command Prompt is an easy and effective way to share your internet connection with other devices. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create a hotspot in just a few minutes, enhancing your connectivity options whether at home or on the go. Don't hesitate to explore this feature and enjoy seamless internet sharing!
FAQs
1. Can I set up a wireless hotspot on Windows 7?
Yes, the process is similar, but the commands may vary slightly. Ensure you have the right drivers installed.
2. Is there a limit to how many devices can connect to my hotspot?
Yes, the number of devices that can connect depends on your internet connection and the capabilities of your network adapter.
3. Can I use my mobile data to create a hotspot?
Yes, if your laptop has a mobile data connection, you can share that connection just like any other internet connection.
4. What if the command prompt returns an error?
Check your network adapter settings and ensure you have administrative privileges. Ensure your wireless card supports hosted networks.
5. Will creating a hotspot affect my internet speed?
Yes, sharing your connection may reduce speed for all connected devices, especially if many devices are using the connection simultaneously.
6. Do I need special software to create a hotspot?
No, Windows has built-in capabilities to create a hotspot through Command Prompt.
7. How do I stop the hotspot?
Run the command
netsh wlan stop hostednetworkin Command Prompt.
8. Can I customize the hotspot settings?
Yes, you can change the SSID and password by re-running the command in Step 3 with new values.
9. Is it safe to share my internet connection?
While it can be safe, ensure you use a strong password to prevent unauthorized access.
10. What should I do if my hotspot disconnects frequently?
Check for driver updates, ensure your PC is not going into sleep mode, and consider the number of devices connected.
Random Reads
- How to set up intex easy set pool
- How to set up internet connection
- How to hang wall cabinets
- How to hang wind chimes
- How to make sure a corner is square with the 3 4 5 rule
- How to take apart xbox one controller
- How to take keys off mechanical keyboard
- How to spot a fake id
- How to spot a spy
- How to split pdf files