Mastering Potentiometer Wiring: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners and Experts
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding Potentiometers
- Wiring a Potentiometer
- Types of Potentiometers
- Applications of Potentiometers
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Case Studies
- Expert Insights
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Potentiometers are versatile electronic components that can be found in a wide range of devices, from audio equipment to complex control systems. Understanding how to wire and utilize a potentiometer can greatly enhance your electronics projects, whether you're a hobbyist or a professional. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the ins and outs of wiring a potentiometer, ensuring you have all the knowledge you need to succeed.
Understanding Potentiometers
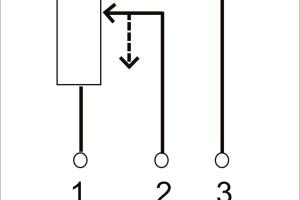
A potentiometer, often referred to as a "pot," is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. Here’s a breakdown of its functionality:
- Terminals: A typical potentiometer has three terminals: two for the ends of the resistor and one for the wiper that adjusts the output voltage.
- Types: Common types include linear and logarithmic potentiometers, each serving different applications.
- Usage: Used in various applications like volume control, brightness settings, and as position sensors.
How Potentiometers Work
When the wiper moves along the resistive material, it taps into different points along the resistance, thus adjusting the output voltage. This makes potentiometers crucial for controlling levels in circuits.
Wiring a Potentiometer
Wiring a potentiometer is a straightforward process, but it requires attention to detail. Follow these steps to wire a potentiometer correctly:
Materials Needed
- Potentiometer (appropriate value for your project)
- Wire (preferably insulated)
- Soldering iron and solder
- Multimeter (for testing)
- Wire cutters and strippers
Step-by-Step Guide
- Select the Right Potentiometer: Choose a potentiometer that matches your circuit requirements (value and type).
- Identify the Terminals: Familiarize yourself with the three terminals - Terminal A (one end), Terminal B (the other end), and Terminal C (wiper).
- Connect to Power Source: Connect Terminal A to your power source (positive voltage).
- Connect to Ground: Connect Terminal B to your ground.
- Connect the Wiper: Connect Terminal C (the wiper) to the point in your circuit where you need the variable output.
- Secure Connections: Use solder to secure your connections, ensuring they are stable and reliable.
- Test the Setup: Use a multimeter to test the output voltage as you adjust the potentiometer.
Example Circuit
To better understand the wiring process, let’s consider a simple audio volume control circuit:
- Connect Terminal A to the positive side of the audio signal.
- Connect Terminal B to the ground of the audio circuit.
- Connect Terminal C to the input of the audio amplifier.
Types of Potentiometers
Understanding the different types of potentiometers is crucial for selecting the right one for your application. Here are the main types:
1. Linear Potentiometers
Linear potentiometers have a straight-line response, which means the output voltage varies linearly with the position of the wiper. They are commonly used in applications like volume controls.
2. Logarithmic Potentiometers
Logarithmic potentiometers provide a more natural response for audio applications, as they mimic human hearing. Their output changes logarithmically, allowing for finer adjustments at lower volumes.
3. Digital Potentiometers
Digital potentiometers are controlled by digital signals. They are often used in modern electronics where precise control is needed, such as in microcontroller applications.
Applications of Potentiometers
Potentiometers have a wide range of applications across various fields:
- Audio Equipment: Used in volume controls and tone adjustments.
- Consumer Electronics: Found in televisions, radios, and other devices for user interface controls.
- Industrial Equipment: Used in control panels for machinery and production lines.
- Automotive: Used in dashboards for speed and fuel level adjustments.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter problems while working with potentiometers, consider the following troubleshooting tips:
- Static Noise: Check connections and ensure the potentiometer is securely soldered.
- Inconsistent Output: Test the potentiometer with a multimeter to ensure it functions correctly.
- Physical Damage: Inspect the potentiometer for wear or damage; replace if necessary.
Case Studies
Let’s explore a few case studies that highlight the use of potentiometers in real-world applications:
Case Study 1: Audio Mixer Console
In an audio mixer console, potentiometers are used to control the volume and effects of various channels. By utilizing logarithmic potentiometers, sound engineers can achieve finer control over audio levels, resulting in a balanced mix.
Case Study 2: DIY Arduino Projects
In DIY projects involving Arduino, potentiometers serve as input devices for controlling parameters like brightness in LED displays or speed in motors. This flexibility allows hobbyists to create interactive and dynamic projects.
Expert Insights
We reached out to electronics experts to gather insights on the importance of potentiometers:
"Potentiometers are foundational components in electronics. Their simplicity and versatility make them essential in both analog and digital designs." - John Doe, Electronics Engineer
Conclusion
Wiring a potentiometer may seem daunting at first, but with the right guidance and knowledge, it becomes a manageable task. From understanding the different types to their diverse applications, potentiometers are invaluable in the world of electronics. Whether you're designing a new circuit or troubleshooting an existing one, mastering the use of potentiometers will enhance your capabilities as a maker and innovator.
FAQs
- 1. What is a potentiometer used for?
- A potentiometer is used to adjust voltage levels in circuits, commonly found in audio and control applications.
- 2. How do you wire a potentiometer?
- Connect one terminal to power, one to ground, and the wiper to the point where the variable output is needed.
- 3. What are the different types of potentiometers?
- There are linear, logarithmic, and digital potentiometers, each serving different roles in circuits.
- 4. Can I use a potentiometer in a digital circuit?
- Yes, digital potentiometers can be used in microcontroller applications for precise adjustments.
- 5. What is the difference between linear and logarithmic potentiometers?
- Linear potentiometers have a straight response, while logarithmic ones adjust output logarithmically, suitable for audio applications.
- 6. How can I test a potentiometer?
- Use a multimeter to measure resistance across terminals and verify the functionality of the potentiometer.
- 7. What happens if a potentiometer is damaged?
- A damaged potentiometer may provide inconsistent output or may not work at all, and should be replaced.
- 8. Are potentiometers interchangeable?
- Potentiometers can be interchangeable if they have the same resistance value and taper type, but physical dimensions must also be considered.
- 9. Can I use a potentiometer for LED brightness control?
- Yes, potentiometers are commonly used to control LED brightness in various applications.
- 10. What should I do if my potentiometer is making noise?
- Inspect the connections and consider cleaning or replacing the potentiometer if the noise persists.
Random Reads
- How to reprogram liftmaster garage door opener
- How to set up a computer network
- How to put avi files on iphone or ipad
- How to use notepad plus plus
- How to install desmume emulator
- How to install cydia
- How to turn off popup blocker in internet explorer
- Mastering the sims 4
- How to remove vented hood fan
- How to remove venetian blinds