Mastering Amperage Calculations: A Comprehensive Guide to Watts, Volts, & Ohm's Law
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding Basic Concepts
- Ohm's Law Explained
- Calculation Methods
- Using an Ammeter
- Real-World Examples
- Case Studies
- Expert Insights
- FAQs
Introduction
Understanding amperage calculations is essential for anyone involved in electrical engineering, electronics, or even DIY projects at home. Whether you're a student, a professional technician, or a hobbyist, grasping the concepts of Watts, Volts, and Ohm's Law is crucial for success. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore these fundamental concepts, provide detailed calculations, and offer practical examples to help you master the art of amperage calculations.
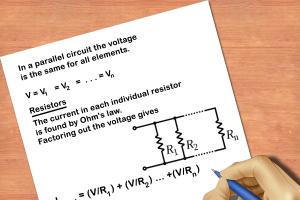
Understanding Basic Concepts
Before diving into calculations, let's break down the fundamental concepts of electricity:
- Voltage (V): The electrical potential difference between two points, measured in volts.
- Current (I): The flow of electric charge, measured in amperes (A).
- Resistance (R): The opposition to current flow in a circuit, measured in ohms (Ω).
- Power (P): The rate at which electrical energy is consumed or produced, measured in watts (W).
Ohm's Law Explained
One of the cornerstones of electrical theory is Ohm's Law, which states that the current (I) through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the conductor. This relationship can be expressed by the formula:
V = I × R
Rearranging this formula can help us find other values:
- I = V / R
- R = V / I
Calculation Methods
Understanding how to perform calculations using the above formulas is essential. Here are some examples:
Calculating Current (I)
To find the current flowing through a circuit, you can use the rearranged Ohm's Law:
I = V / R
For instance, if you have a circuit with a voltage of 12 volts and a resistance of 4 ohms:
I = 12V / 4Ω = 3A
Calculating Voltage (V)
To calculate voltage, rearrange the formula as follows:
V = I × R
If the current is 2 amperes and the resistance is 5 ohms:
V = 2A × 5Ω = 10V
Calculating Resistance (R)
Finally, to find resistance, use:
R = V / I
If the voltage is 24 volts and the current is 6 amperes:
R = 24V / 6A = 4Ω
Using an Ammeter
An ammeter is a device used to measure the current (amperage) flowing through a circuit. Here’s how to properly use an ammeter:
Step-by-Step Guide
- Turn Off Power: Before connecting the ammeter, ensure that the circuit is powered off to avoid damage or injury.
- Connect the Ammeter: Disconnect the circuit at the point where you want to measure the current. Connect the ammeter in series with the circuit component to complete the circuit.
- Power On: Turn the power back on and observe the reading on the ammeter.
- Record the Value: Note the current reading displayed on the ammeter.
Real-World Examples
To further solidify your understanding, let's look at practical examples of applying Ohm's Law and calculations in real-world scenarios:
Example 1: Light Bulb Circuit
Consider a 60-watt incandescent light bulb running on a 120-volt circuit. To find out how much current the bulb draws:
P = V × I => I = P / V
I = 60W / 120V = 0.5A
Example 2: Electric Heater
If an electric heater operates at 1500 watts and is plugged into a 240-volt outlet, we can find the current:
I = P / V
I = 1500W / 240V = 6.25A
Case Studies
Examining case studies can provide insights into the practical applications of amperage calculations:
Case Study 1: Residential Wiring
In a house with multiple appliances, understanding how to calculate total amperage is crucial for safety and functionality. For example, a kitchen circuit may have a refrigerator (2A), microwave (10A), and dishwasher (8A). The total current would be:
Total I = 2A + 10A + 8A = 20A
Case Study 2: Solar Power System
In a solar power installation, you need to calculate the total current output of solar panels. If you have four panels producing 250W each at a system voltage of 48V:
Total P = 4 × 250W = 1000W
I = P / V = 1000W / 48V = 20.83A
Expert Insights
According to electrical engineers, accurate calculations of amperage are vital for ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. Understanding the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance allows technicians to troubleshoot issues effectively.
"Every electrical circuit behaves differently, and knowing how to calculate these values is essential for preventing overloads and ensuring optimal performance," says a leading electrical engineer.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between volts, amps, and watts?
Volts measure electrical potential, amps measure current flow, and watts measure power consumption.
2. How do you calculate amperage from watts and voltage?
Use the formula I = P / V, where I is current in amps, P is power in watts, and V is voltage in volts.
3. Can I measure current with a multimeter?
Yes, a multimeter can measure current by being placed in series with the circuit.
4. What happens if I connect an ammeter directly across a voltage source?
This can cause a short circuit, potentially damaging the ammeter and creating a hazardous situation.
5. How do I calculate resistance if I know voltage and current?
Use the formula R = V / I, where R is resistance in ohms, V is voltage in volts, and I is current in amps.
6. What are typical amperage ratings for household circuits?
Standard household circuits typically range from 15A to 20A for general-purpose circuits.
7. Why is it important to understand amperage calculations?
Understanding amperage calculations helps prevent electrical overloads and ensures safe operation of electrical devices.
8. Can I use Ohm's Law for AC circuits?
Yes, Ohm's Law applies to both AC and DC circuits, although AC circuits may also involve impedance.
9. How can I improve my understanding of electrical calculations?
Practice with real-world examples, take online courses, or consult with professionals in the field.
10. What tools do I need for measuring electrical values?
A multimeter is essential for measuring voltage, current, and resistance in various electrical circuits.
Random Reads
- Mastering the grand exchange runesape guide
- Mastering image downloads
- Mastering google voice texting
- Ultimate guide limescale removal
- How to log in to telegram web
- How to lock folder batch file
- How to see street view google maps iphone ipad
- Mastering screenshots
- How to install vinyl siding
- How to install windows 7 using pen drive