Mastering the Art of Total Current Calculation: A Comprehensive Guide
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding Current
- Theories and Principles of Current
- Ohm's Law Explained
- Calculating Total Current
- Examples of Total Current Calculation
- Real-World Case Studies
- Expert Insights on Total Current
- Common Mistakes in Current Calculation
- FAQs
Introduction
Understanding how to calculate total current is essential for anyone working in electrical engineering, physics, or related fields. Total current, often denoted by 'I', is the flow of electric charge in a circuit and is measured in amperes (A). This comprehensive guide will delve into the definitions, formulas, and practical applications of total current, providing you with the tools you need to master this crucial concept.
Understanding Current
Current is defined as the rate at which electric charge flows through a conductor. It can be classified into two main types:
- Direct Current (DC): Electric charge flows in one direction, commonly used in batteries.
- Alternating Current (AC): Electric charge changes direction periodically, used in household power supplies.
Understanding these types is foundational for calculating total current in various scenarios.
Theories and Principles of Current
Several fundamental theories and principles guide our understanding of current, including:
- Charge: The basic property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field.
- Voltage: The electrical potential difference between two points, influencing how much current flows.
- Resistance: The opposition to the flow of current, measured in ohms (Ω).
Ohm's Law Explained
Ohm's Law is a fundamental equation in electrical engineering represented as:
I = V/R
Where:
- I = current (A)
- V = voltage (V)
- R = resistance (Ω)
This law aids in determining total current by rearranging the formula based on the known parameters. Understanding this formula is crucial for accurate current calculations.
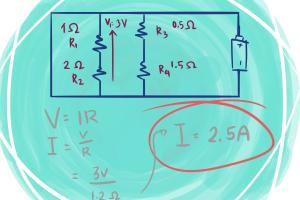
Calculating Total Current
Calculating total current involves understanding the circuit configuration, which can be in series, parallel, or a combination of both. Let’s break down the calculations:
1. Series Circuits
In a series circuit, the total current is the same through all components. The formula can be represented as:
Itotal = I1 = I2 = I3
Where each I represents the current through each component.
2. Parallel Circuits
In parallel circuits, the voltage across each component is the same, and total current can be calculated using:
Itotal = I1 + I2 + I3
This means the total current is the sum of the currents through each parallel branch.
3. Combination Circuits
For circuits that have both series and parallel components, first calculate the current in the series groups and then use that to determine the total current in parallel branches.
Examples of Total Current Calculation
Example 1: Series Circuit Calculation
Consider a series circuit with a 12V battery and two resistors of 4Ω and 8Ω. The total resistance (Rtotal) is:
Rtotal = R1 + R2 = 4Ω + 8Ω = 12Ω
Using Ohm’s Law:
Itotal = V/Rtotal = 12V / 12Ω = 1A
Example 2: Parallel Circuit Calculation
For a parallel circuit with a 9V battery and two branches with resistors of 3Ω and 6Ω, the total current is calculated as:
I1 = V/R1 = 9V / 3Ω = 3A
I2 = V/R2 = 9V / 6Ω = 1.5A
Itotal = I1 + I2 = 3A + 1.5A = 4.5A
Real-World Case Studies
Understanding total current isn't just academic; it's vital in real-world applications. Here are two case studies highlighting the importance of accurate current calculations:
Case Study 1: Home Electrical Wiring
A homeowner experienced frequent circuit breaker trips. After investigation, it was found that the total current exceeded the circuit's capacity due to multiple devices drawing power simultaneously. Properly calculating total current helped the electrician recommend a suitable circuit upgrade.
Case Study 2: Industrial Applications
In a manufacturing plant, machinery operating on a common circuit faced performance issues. Calculating total current allowed engineers to balance the load effectively, preventing overload and enhancing productivity.
Expert Insights on Total Current
Experts emphasize the importance of understanding the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. Regular training in circuit analysis and current calculation techniques is recommended to ensure safety and efficiency in electrical work.
Common Mistakes in Current Calculation
Here are some common pitfalls to avoid when calculating total current:
- Neglecting the impact of resistance on current flow.
- Failing to account for all branches in parallel circuits.
- Overlooking the implications of voltage drops across components.
FAQs
1. What is total current?
Total current is the flow of electric charge in a circuit, measured in amperes (A).
2. How do I calculate total current in a series circuit?
In a series circuit, total current is the same through all components and can be calculated using Ohm's Law.
3. How is total current calculated in a parallel circuit?
Total current in a parallel circuit is the sum of the currents through each branch.
4. What is the importance of calculating total current?
Calculating total current is crucial for ensuring circuit safety and functionality, preventing overloads and equipment damage.
5. Can total current exceed the circuit's limit?
Yes, exceeding the circuit's limit can lead to tripped breakers or electrical fires.
6. What tools are needed to measure current?
Common tools include multimeters and ammeters, which can measure current in various circuit configurations.
7. What happens if I miscalculate total current?
Miscalculating total current can result in circuit failures, equipment damage, or safety hazards.
8. How can I improve my current calculation skills?
Practice with real-world examples, take courses on electrical engineering, and use simulation software.
9. Is current the same as voltage?
No, current (I) is the flow of electric charge, while voltage (V) is the potential difference that drives the current.
10. What are the units for measuring current?
Current is measured in amperes (A), where 1 ampere equals the flow of one coulomb of charge per second.
For further reading and exploration of electrical concepts, check out these authoritative sources:
- Understanding Amps, Volts, and Ohms
- What is Current? - Electrical4U
- Current and Voltage in Circuits - Electronics Tutorials
Random Reads
- How to convert watts to amps
- Ultimate guide installing software linux
- How to paint a refrigerator
- How to organize chrome bookmarks
- Twitch logs check
- Turn off location sharing iphone
- How to wax wooden furniture
- How to waterproof your basement
- Ultimate guide destroying hard drives
- How to convert inches to feet