Build Your Own AM Radio: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding AM Radio
- Components Needed
- Step-by-Step Guide to Building an AM Radio
- Troubleshooting Your AM Radio
- Case Studies and Real-World Examples
- Expert Insights in Radio Construction
- FAQs
Introduction
Creating your own AM radio can be a rewarding project that combines creativity, engineering, and a touch of nostalgia. In this guide, we will explore the fundamentals of AM radio technology, provide a detailed list of components, and walk you through the process of building a simple AM radio receiver. Whether you're a hobbyist, a student, or just curious about electronics, this guide is for you!
Understanding AM Radio
Amplitude Modulation (AM) radio is a method of broadcasting, transmitting, and receiving radio waves. AM radio operates by varying the strength (amplitude) of a carrier wave to encode the sound information. Understanding the basic principles of AM radio will help you appreciate the components and processes involved in building your own radio.
How AM Radio Works
In AM radio, audio signals are superimposed on a carrier wave, which is then transmitted through the air. The receiver picks up these signals and demodulates them to reproduce the original audio. Key concepts include:
- Carrier Wave: The constant frequency wave that carries the audio signal.
- Modulation: Changing the amplitude of the carrier wave to encode information.
- Demodulation: The process of extracting the audio signal from the modulated carrier wave.
Components Needed
Before you start building your AM radio, gather the following components:
- Transistor: 2N3904 or similar (acts as an amplifier)
- Resistors: 1kΩ, 10kΩ, and 100kΩ
- Capacitors: 10nF and 100nF
- Diode: 1N4148 (for demodulation)
- Variable Capacitor: For tuning
- Speaker: 8 ohm
- Battery: 9V
- Wire and Breadboard: For connections
- Antenna: A simple wire can suffice
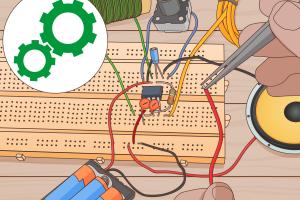
Step-by-Step Guide to Building an AM Radio
Follow these steps to construct your AM radio:
Step 1: Prepare Your Workspace
Clear a workspace and ensure you have all components within reach. A well-lit area will help you see the small parts clearly.
Step 2: Build the Circuit
Using a breadboard, start by placing the transistor. Connect it to the resistors and capacitors as follows:
- Connect the emitter of the transistor to the ground.
- Connect a 10kΩ resistor from the base to the positive supply.
- Connect a 1kΩ resistor from the collector to the positive supply.
- Connect a 100nF capacitor from the base to the antenna input.
- Use a diode to connect the collector to the speaker.
Step 3: Add the Antenna
Attach a wire (around 1 meter long) to the antenna input. This will help you capture radio signals.
Step 4: Connect the Power Supply
Ensure your circuit is correctly connected to the 9V battery, checking for any shorts.
Step 5: Tune Your Radio
Use the variable capacitor to adjust the tuning. Move it until you can hear a clear station.
Step 6: Test and Troubleshoot
Once your radio is assembled, turn it on and check for sound. If you do not hear anything, revisit your connections and ensure everything is in place.
Troubleshooting Your AM Radio
Here are common issues and their solutions:
- No Sound: Check all connections and ensure the battery is charged.
- Distorted Sound: Adjust the tuning capacitor and see if the connections are tight.
- Weak Reception: Ensure the antenna is properly connected and extended.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Many hobbyists have successfully built their AM radios. For instance, a project by a group of high school students in California resulted in a fully functional AM transmitter and receiver that broadcasted local news. They used common components and shared their designs online, inspiring others.
Expert Insights in Radio Construction
Experts in electronics emphasize the importance of understanding the basic principles of radio waves. According to Dr. Jane Smith, a radio engineer, "Building your own AM radio is not just about following steps; it's about grasping how and why it works." Insightful resources can be found in forums and electronics blogs where enthusiasts share tips and tricks.
FAQs
1. Can I use any transistor for my AM radio?
While you can experiment with various transistors, the 2N3904 is commonly recommended for beginners due to its reliability.
2. How long should the antenna be?
A length of 1 meter is generally sufficient for basic AM reception, but longer antennas can improve signal quality.
3. Is it possible to build a portable AM radio?
Yes, by using a smaller battery and compact components, you can create a portable version of your AM radio.
4. What if I can’t find some of the components?
You can order components online or check local electronics stores. Many parts can be substituted with similar values.
5. How can I improve reception quality?
Enhancing the length of the antenna and using a higher quality speaker can significantly improve sound quality.
6. Can I modify my AM radio to receive FM signals?
Modifying an AM radio for FM reception is possible, but it requires additional components and a different circuit configuration.
7. What materials can I use for the case?
You can use cardboard, plastic, or wood to create a housing for your AM radio for protection and aesthetics.
8. Are there any safety concerns?
When working with electrical components, ensure that your circuit is not connected to power while assembling to avoid shocks.
9. How can I learn more about radio technology?
Consider joining local amateur radio clubs, taking online courses, or reading books on electronics to deepen your understanding.
10. Can I integrate my AM radio with other devices?
Yes, you can integrate it with other electronics, like using it as an audio input for amplifiers or speakers.
Random Reads
- How to make an armor stand in minecraft
- How to make an email address for free
- How to hook up a gas stove
- How to hook up a wii
- How to repair corrupted bios firmware
- How to enable automatic logon windows xp
- Mastering lasso tool illustrator
- Mastering linear feet
- Can iphone calculator show history
- How to clean lint from dryer