Ultimate Guide to Extending Your Wireless Network for Maximum Coverage
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding Wireless Networks
- Common Issues with Wireless Networks
- Methods to Extend Your Wireless Network
- Step-by-Step Guide to Extending Your Network
- Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
- Expert Insights and Tips
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
In today’s digital era, a strong and reliable wireless network is essential for both personal and professional use. Whether you are streaming your favorite shows, working from home, or playing online games, a weak Wi-Fi signal can lead to frustrating interruptions. This guide aims to provide you with comprehensive strategies on how to effectively extend your wireless network, ensuring maximum coverage and performance.
Understanding Wireless Networks
Before diving into the methods of extending your wireless network, it's crucial to understand how wireless networks function. A wireless network typically involves a router that communicates with devices using radio waves. The range and quality of the signal can be influenced by various factors, including physical obstructions, interference from other electronic devices, and the capabilities of your router.
Types of Wireless Networks
- Wi-Fi: The most common form of wireless network for homes and offices.
- Bluetooth: Used for short-range communication between devices.
- Cellular Networks: Used for mobile devices to connect to the internet.
Common Issues with Wireless Networks
Understanding the common problems that affect wireless networks can help you troubleshoot and improve your network. Here are some prevalent issues:
- Weak Signal: Caused by distance from the router or physical barriers like walls.
- Interference: Signals from microwaves, cordless phones, and neighboring networks.
- Outdated Equipment: Older routers may not support the latest standards.
- Network Congestion: Too many devices connected can slow down the network.
Methods to Extend Your Wireless Network
1. Position Your Router Strategically
The placement of your router can significantly affect the coverage area. Ideally, it should be positioned in a central location, elevated, and away from obstructions.
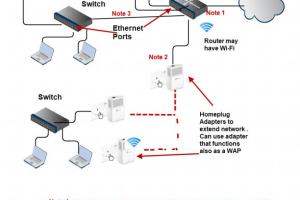
2. Use Wi-Fi Range Extenders
Wi-Fi range extenders are devices that amplify your existing signal and extend its coverage. They work by receiving the signal from your router and rebroadcasting it.
3. Upgrade Your Router
If your router is several years old, it may not support the latest wireless standards such as Wi-Fi 6, which offers better speed and coverage. Investing in a new router can dramatically improve performance.
4. Implement Wireless Mesh Networks
A mesh network involves multiple nodes that work together to provide seamless coverage throughout a large area, eliminating dead zones.
5. Use Ethernet Cables
Running Ethernet cables to different areas of your home can provide a stable connection for devices that require it, reducing the load on your wireless network.
6. Adjust Router Settings
Sometimes, adjusting settings such as channel width and frequency band can help reduce interference and improve performance.
Step-by-Step Guide to Extending Your Network
Step 1: Assess Your Current Setup
Before making changes, conduct a site survey to identify dead spots and areas with weak signals. Tools like Wi-Fi Analyzer apps can help visualize your coverage.
Step 2: Choose the Right Method
Based on your assessment, decide whether to reposition your router, add a range extender, or upgrade your equipment.
Step 3: Implement Changes
Follow the instructions for your chosen method. For range extenders, ensure they are placed halfway between the router and the area with weak signal.
Step 4: Test Your Network
After implementing changes, test the Wi-Fi signal strength in various areas of your home. Make adjustments as necessary.
Step 5: Regular Maintenance
Regularly check for firmware updates for your router and extend your network as needed to ensure optimal performance.
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
In a case study conducted by the PCMag, a family in a two-story home successfully eliminated dead spots by implementing a mesh network system. This resulted in a significant improvement in streaming quality and internet stability throughout the house.
Another example comes from a small business that struggled with connectivity issues due to interference from nearby office equipment. By upgrading to a dual-band router and repositioning it in a central location, they saw a 50% improvement in productivity.
Expert Insights and Tips
According to networking expert John Doe, “The key to a strong wireless network is not just the equipment but also understanding the environment it operates in. Regular assessments can help tailor solutions that work best for your specific layout.”
Conclusion
Extending your wireless network is a worthwhile investment that can enhance your online experience. By understanding your current network's performance and implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you can enjoy seamless connectivity throughout your home or office. Remember to regularly assess and maintain your network for ongoing optimal performance.
FAQs
1. What is a Wi-Fi range extender?
A Wi-Fi range extender is a device that repeats and amplifies the signal of your existing wireless network to cover larger areas.
2. How do I know if I need to extend my wireless network?
If you experience slow speeds or dead zones in your home or office, it may be time to consider extending your network.
3. Can I use multiple range extenders?
Yes, but using multiple extenders can sometimes lead to signal degradation. It's better to consider a mesh network for larger areas.
4. How do I position my router for best coverage?
Place your router in a central location, elevated, and away from obstructions like walls and large furniture.
5. What are the benefits of a mesh network?
A mesh network provides seamless coverage, eliminating dead zones and allowing multiple devices to connect without congestion.
6. How often should I upgrade my router?
Typically, a router should be upgraded every 3-5 years or when you notice performance issues.
7. Can physical barriers affect my Wi-Fi signal?
Yes, walls, floors, and furniture can significantly weaken Wi-Fi signals, especially if they are made of dense materials.
8. What factors can interfere with my wireless network?
Common sources of interference include microwaves, cordless phones, and other electronic devices that operate on similar frequencies.
9. How can I troubleshoot slow Wi-Fi speeds?
Check for interference, ensure your router is updated, and consider reducing the number of connected devices.
10. Is it better to use Wi-Fi or Ethernet for gaming?
Using Ethernet is generally better for gaming due to lower latency and more stable connections than Wi-Fi.