Ultimate Guide: How to Save Files to a USB Flash Drive for Beginners
-
Quick Links:
- What is a USB Flash Drive?
- Why Use a USB Flash Drive?
- Choosing the Right USB Flash Drive
- How to Save Files to a USB Flash Drive: Step-by-Step Guide
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Best Practices for USB Flash Drive Use
- FAQs
What is a USB Flash Drive?
A USB flash drive, also known as a thumb drive or pen drive, is a compact portable storage device that connects to computers and other devices via a USB port. These devices typically range in storage capacity from 2GB to 2TB, providing ample space for various files like documents, photos, and videos.
Why Use a USB Flash Drive?
USB flash drives offer numerous benefits:
- Portability: Their small size makes them easy to carry.
- Durability: Unlike hard drives, flash drives have no moving parts, making them less prone to mechanical failure.
- Ease of Use: They can be easily plugged in and out, making file transfer straightforward.
- Compatibility: Most modern devices support USB connections, ensuring wide compatibility.
Choosing the Right USB Flash Drive
Selecting the right USB flash drive depends on several factors:
- Storage Capacity: Choose based on your storage needs (e.g., 16GB for documents, more for videos).
- Speed: Look for USB 3.0 or 3.1 for faster data transfer rates.
- Durability: Consider rugged models if you plan to use it in harsh conditions.
- Brand Reputation: Choose established brands known for quality and reliability.
How to Save Files to a USB Flash Drive: Step-by-Step Guide
Follow these steps to save files to your USB flash drive:
Step 1: Insert the USB Flash Drive
Locate the USB port on your computer and insert the USB flash drive. Wait for the system to recognize it.
Step 2: Open File Explorer (Windows) or Finder (Mac)
On Windows, press Windows + E to open File Explorer. On a Mac, click on the Finder icon in the dock.
Step 3: Find Your Files
Navigate to the folder containing the files you wish to transfer.
Step 4: Copy Files
Select the files, then right-click and choose Copy or press Ctrl + C (Windows) or Command + C (Mac).
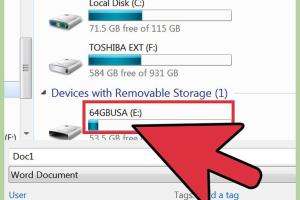
Step 5: Open the USB Flash Drive
In File Explorer or Finder, locate your USB flash drive listed under "This PC" or "Devices." Click to open it.
Step 6: Paste the Files
Right-click in the USB drive window and select Paste, or use Ctrl + V (Windows) or Command + V (Mac).
Step 7: Eject the USB Flash Drive
Once the files are transferred, safely eject the drive by right-clicking on it and selecting Eject. Wait for a notification before physically removing the drive.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While using USB flash drives, you may encounter common issues:
- Drive Not Recognized: Ensure the USB port is functioning and try a different port or computer.
- Write Protection: Some drives have a physical switch; check if it’s turned on.
- File Transfer Errors: Ensure there’s enough space on the USB drive and that files aren’t corrupted.
Best Practices for USB Flash Drive Use
To maximize the lifespan and effectiveness of your USB flash drive:
- Keep It Clean: Store it in a protective case to avoid dust and physical damage.
- Regular Backups: Don’t rely solely on a USB drive; back up files on multiple devices.
- Safely Eject: Always eject the drive before removing it to prevent data corruption.
- Use Encryption: For sensitive data, consider encrypting your files for added security.
FAQs
1. What types of files can I save on a USB flash drive?
You can save virtually any type of file, including documents, images, videos, and software applications.
2. Can I use a USB flash drive on different operating systems?
Yes, most USB flash drives are compatible with Windows, macOS, and Linux.
3. How do I know if my USB drive is full?
Check the available space by right-clicking on the drive in File Explorer or Finder and selecting Properties or Get Info.
4. Is it safe to store sensitive information on a USB drive?
While it is generally safe, consider encrypting sensitive data for additional security.
5. What happens if I accidentally remove the USB drive during a transfer?
This can lead to data corruption. Always ensure the transfer is complete and safely eject the drive.
6. Can I recover files from a corrupted USB flash drive?
It may be possible with data recovery software, but success is not guaranteed.
7. How long do USB flash drives last?
With proper care, USB flash drives can last for several years, but frequent write and erase cycles can impact their lifespan.
8. Are there any size limitations for files saved on a USB drive?
File size limits depend on the file system (e.g., FAT32 has a 4GB limit per file).
9. Can I use a USB flash drive for booting an operating system?
Yes, many users create bootable USB drives to install operating systems or run live environments.
10. What should I do if my USB drive is not showing up on my computer?
Try a different USB port, check Disk Management on Windows, or run hardware diagnostics.
Conclusion
Saving files to a USB flash drive is a straightforward process that enhances data portability and accessibility. By following the steps outlined in this guide, users can effectively manage their files and maximize the utility of their USB devices. Remember to take proper care of your flash drive to ensure it serves you well for years to come.
References
- Lifewire: How to Use a USB Flash Drive
- How-To Geek: How to Use a USB Flash Drive
- PC Gamer: How to Use a USB Flash Drive
- TechRadar: How to Use a USB Flash Drive
- Digital Trends: How to Use a USB Flash Drive
Random Reads