Mastering GParted: A Comprehensive Guide to Partition Management
GParted, or GNOME Partition Editor, is a powerful tool for managing disk partitions in Linux and other operating systems. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about using GParted, from installation to advanced features, to help you manage your partitions efficiently.
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction to GParted
- Installing GParted
- Understanding the GParted Interface
- Basic Operations in GParted
- Advanced Features of GParted
- Case Studies: Practical Applications of GParted
- Expert Insights on Disk Management
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Best Practices for Using GParted
- FAQs
Introduction to GParted
GParted is an open-source partition editor used for tasks such as resizing, moving, and creating partitions on your hard drive. It supports various file systems and is a go-to tool for anyone looking to manage their disk space efficiently. Whether you're a casual user trying to free up space or an IT professional managing multiple systems, GParted provides the necessary tools you need.
Installing GParted
Installing GParted is straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
For Linux Users
- Open your terminal.
- Update your package list with:
sudo apt update - Install GParted using:
sudo apt install gparted - Once installed, you can launch it by typing
gpartedin the terminal or finding it in your applications menu.
For Windows Users
While GParted is primarily a Linux tool, you can use it through a live USB or CD. Here’s how:
- Download the GParted Live ISO from the official website: GParted Download
- Create a bootable USB using tools like Rufus or UNetbootin.
- Boot from the USB and select GParted from the menu.
Understanding the GParted Interface
The GParted interface is user-friendly, but it’s essential to understand its components:
- Menu Bar: Access to file operations, edit, view, and help options.
- Partition Table: Displays all partitions on your selected disk.
- Partition Information Pane: Shows details like size, used space, file system, and flags.
Basic Operations in GParted
Creating a New Partition
To create a new partition, follow these steps:
- Select the unallocated space in the partition table.
- Right-click and select New.
- Specify the size, file system type, and label, then click Add.
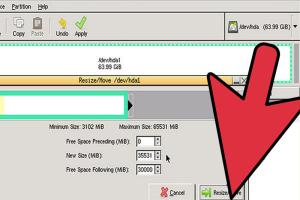
Resizing a Partition
To resize a partition:
- Right-click on the partition you wish to resize.
- Select Resize/Move.
- Adjust the size by dragging the edges or entering a new size.
- Click Resize/Move to apply the changes.
Deleting a Partition
To delete a partition, simply:
- Right-click the partition you want to delete.
- Select Delete.
- Confirm the deletion when prompted.
Advanced Features of GParted
File System Check
GParted allows you to check and repair file systems. To do this:
- Right-click on the partition.
- Select Check.
- GParted will run a diagnostic and attempt to fix any issues.
Copying and Cloning Partitions
You can easily copy and clone partitions using GParted:
- Right-click on the source partition and select Copy.
- Right-click on the destination and select Paste.
Case Studies: Practical Applications of GParted
Case Study 1: Dual-Boot Setup
A user wanted to set up a dual-boot system with Windows and Linux. They used GParted to resize the Windows partition and create space for the Linux installation.
Case Study 2: Data Recovery
After accidental deletion of a partition, a user utilized GParted to recover data from the unallocated space, demonstrating the importance of having GParted ready for emergencies.
Expert Insights on Disk Management
According to experts, managing disk partitions effectively can optimize system performance. Regular checks and maintenance via GParted can prevent data loss and improve overall system health.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While GParted is a robust tool, users may encounter issues:
Partition Not Resizing
This can occur if the partition is mounted. Ensure that you unmount the partition before attempting to resize it.
Data Loss Risk
Always back up your data before making changes to partitions. GParted is powerful but not infallible.
Best Practices for Using GParted
- Always back up your data before making any changes.
- Use GParted in a live environment for safety.
- Regularly check the health of your partitions.
- Familiarize yourself with the interface before making changes.
FAQs
1. What is GParted?
GParted is a free, open-source partition editor for managing disk partitions.
2. Can I use GParted on Windows?
Yes, you can use GParted on Windows via a bootable USB or CD.
3. Is GParted safe to use?
While GParted is generally safe, always back up your data before making changes to partitions.
4. What file systems does GParted support?
GParted supports various file systems, including ext2, ext3, ext4, NTFS, FAT16, and FAT32.
5. Can GParted recover lost partitions?
GParted cannot recover lost partitions directly, but it can help manage unallocated space.
6. How do I uninstall GParted?
You can uninstall GParted via your package manager by using the command: sudo apt remove gparted.
7. Is GParted available for macOS?
GParted is not natively available for macOS, but it can be run in a virtual machine or through a live USB.
8. What happens if I forget to unmount a partition?
If you forget to unmount a partition, GParted will not allow you to make changes to it.
9. How can I create a bootable USB for GParted?
You can create a bootable USB using tools like Rufus, UNetbootin, or balenaEtcher.
10. Where can I find help for GParted?
You can find help in the official GParted documentation at GParted Documentation.
By mastering GParted, you can take control of your disk management tasks effectively, ensuring that your data is organized and your system runs smoothly. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced user, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to utilize GParted to its fullest potential.