Mastering GPG: A Comprehensive Guide to Verifying GPG Signatures
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding GPG and Its Importance
- What are GPG Signatures?
- Setting Up GPG
- How to Verify a GPG Signature
- Common Issues in GPG Signature Verification
- Case Studies: Real-World Applications
- Best Practices for GPG Usage
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Introduction
In the realm of cybersecurity, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of digital communications is paramount. One of the most effective tools for achieving this is GPG (GNU Privacy Guard), a powerful encryption tool that allows users to encrypt and sign data and communications. This article will delve deep into the process of verifying GPG signatures, providing a comprehensive step-by-step guide, expert insights, and real-world case studies to help you master this essential skill.
Understanding GPG and Its Importance
GPG is a free implementation of the OpenPGP standard, allowing users to encrypt and sign their messages and files. The ability to verify GPG signatures is crucial for ensuring that the data you receive has not been tampered with and originates from a trusted source. In an era where data breaches and phishing attacks are rampant, understanding how to use GPG effectively can significantly enhance your digital security.
What are GPG Signatures?
A GPG signature is a way to ensure the authenticity and integrity of a message or file. When a user signs a file with their private key, it generates a signature that can be verified by anyone who has access to the user's public key. This process helps to confirm that the message has not been altered and that it originates from the claimed sender.
How GPG Signatures Work
- The sender signs a document using their private key.
- The recipient receives the signed document along with the signature.
- The recipient uses the sender's public key to verify the signature.
Setting Up GPG
Before you can verify a GPG signature, you need to have GPG installed on your system. The installation process varies depending on your operating system, but here are the steps for the major platforms:
Installing GPG on Different Operating Systems
For Windows:
- Download the Gpg4win installer from gpg4win.org.
- Run the installer and follow the prompts to complete the installation.
For macOS:
- Install Homebrew if you haven't already.
- Open the Terminal and run:
brew install gpg.
For Linux:
- Open your terminal.
- Run the following command based on your distribution:
- Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install gnupg - Fedora:
sudo dnf install gnupg
How to Verify a GPG Signature
Once you have GPG installed, follow these steps to verify a GPG signature:
Step 1: Obtain the File and Signature
Make sure you have both the signed file and the corresponding signature file. The signature file usually has a .sig or .asc extension.
Step 2: Import the Signer's Public Key
Before you can verify the signature, you need to have the public key of the person who signed the document. Use the command:
gpg --import publickey.asc
Step 3: Verify the Signature
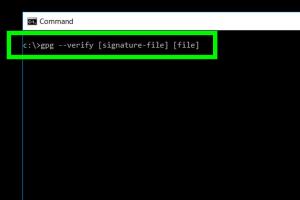
Use the following command to verify the signature:
gpg --verify file.sig file
If the signature is valid, you will see a message indicating that the signature is "Good." If it is invalid, GPG will notify you of this as well.
Step 4: Check for Trust Issues
Even if the signature is verified successfully, you should also check if you trust the signer's public key. GPG allows you to assign trust levels to keys to ensure that you're confident in their authenticity.
Common Issues in GPG Signature Verification
While verifying GPG signatures is generally straightforward, several common issues can arise:
- Missing Public Key: If you haven't imported the signer's public key, GPG cannot verify the signature.
- Expired Key: Public keys can expire. Ensure that the signer's key is still valid.
- Untrusted Key: GPG may indicate that the key is untrusted. This can be resolved by adjusting trust settings.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
To illustrate the importance of verifying GPG signatures, consider the following case studies:
Case Study 1: Software Distribution
Many open-source software projects use GPG signatures to ensure that the software packages distributed to users are genuine and untampered. For instance, the Linux kernel is often validated with GPG signatures to maintain integrity.
Case Study 2: Secure Communications
Organizations that handle sensitive data, such as financial institutions, utilize GPG signatures to secure emails and documents. By verifying signatures, they can maintain confidentiality and ensure that communications have not been intercepted.
Best Practices for GPG Usage
To maximize your security with GPG, consider the following best practices:
- Regularly update your public keys and revocation certificates.
- Use strong, unique passphrases for your private keys.
- Periodically verify and refresh trust in your contacts' public keys.
- Keep your GPG installation up to date to mitigate vulnerabilities.
FAQs
1. What is GPG?
GPG, or GNU Privacy Guard, is an open-source implementation of the OpenPGP standard for data encryption and signing.
2. Why should I verify GPG signatures?
Verifying GPG signatures ensures that the data you receive is authentic and has not been altered.
3. What happens if a GPG signature is invalid?
If a GPG signature is invalid, it indicates that the message may have been tampered with or that it was not signed by the claimed sender.
4. How can I obtain someone's public key?
You can obtain a public key from the person directly or through public key servers.
5. Can I verify multiple signatures at once?
Yes, you can verify multiple signatures by providing the signature files and the corresponding documents in a single command.
6. What should I do if my public key is compromised?
If your public key is compromised, you should revoke it immediately and distribute a new public key.
7. Is GPG suitable for non-technical users?
Yes, while there is a learning curve, various graphical user interfaces make GPG accessible for non-technical users.
8. Can GPG be used for file encryption?
Yes, GPG can be used not only for signing but also for encrypting files to ensure confidentiality.
9. How long does a GPG key last?
GPG keys can be set to expire after a specific period, but you can also set them to never expire.
10. Is it safe to trust public key servers?
While public key servers are useful, you should verify keys through other means before trusting them. Always cross-check with the key owner.
Conclusion
Verifying GPG signatures is a vital skill in maintaining digital security. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure that the data you receive is authentic and secure. As cyber threats continue to evolve, mastering tools like GPG will empower you to protect your communications and data effectively.
Random Reads
- How to turn off a personal computer
- How to use 7 zip to create self extracting executables
- How to install homebrew browser
- How to install hard drive
- How to hide apps on android
- How to hang wall cabinets
- Pairing samsung remote tv troubleshooting
- How to refresh ip address windows
- How to refresh yahoo mail
- How to make a piston in minecraft