How to Properly Wire a GFCI Receptacle: A Step-by-Step Guide for Homeowners
-
Quick Links:
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What is a GFCI Receptacle?
- 3. Importance of GFCI Receptacles
- 4. Tools and Materials Needed
- 5. Safety Precautions
- 6. Step-by-Step Guide to Wiring a GFCI Receptacle
- 7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 8. Case Studies and Real-World Examples
- 9. Expert Insights and Tips
- 10. FAQs
1. Introduction
GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) receptacles are essential components of modern electrical systems, particularly in areas where water and electricity may come into contact. Understanding how to wire a GFCI receptacle properly can not only enhance the safety of your home but also ensure compliance with electrical codes. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about GFCI receptacles, including their significance, wiring instructions, and common mistakes to avoid.
2. What is a GFCI Receptacle?
A GFCI receptacle is a type of electrical outlet designed to protect against electrical shock. It continuously monitors the flow of electricity and can quickly cut off power if it detects an imbalance, such as a ground fault that could lead to electrocution. GFCI receptacles are typically used in areas such as bathrooms, kitchens, basements, and outdoor locations.
3. Importance of GFCI Receptacles
GFCI receptacles play a critical role in electrical safety. According to the Consumer Product Safety Commission, GFCI outlets prevent over 30,000 injuries and hundreds of deaths from electrical shocks each year. By installing GFCI receptacles in your home, you not only comply with local electrical codes but also create a safer environment for you and your loved ones.
4. Tools and Materials Needed
- GFCI receptacle
- Wire stripper
- Flathead screwdriver
- Phillips screwdriver
- Voltage tester
- Electrical tape
- Wire connectors
- Drill (if necessary)
5. Safety Precautions
Before beginning any electrical work, it is crucial to prioritize safety. Here are some essential safety precautions to follow:
- Always turn off the power at the circuit breaker before starting work.
- Use a voltage tester to ensure that the power is off.
- Wear safety goggles and gloves to protect yourself from debris and electric shock.
- Follow all local electrical codes and regulations.
6. Step-by-Step Guide to Wiring a GFCI Receptacle
Step 1: Turn Off the Power
Locate your circuit breaker panel and turn off the circuit that supplies power to the outlet you will be working on.
Step 2: Remove the Existing Outlet
Use a screwdriver to remove the faceplate and unscrew the existing outlet from the electrical box. Carefully pull it out to expose the wiring.
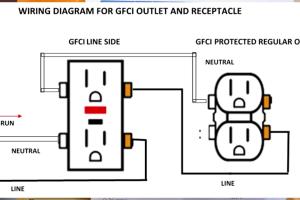
Step 3: Identify the Wires
You should see three wires: a black (hot) wire, a white (neutral) wire, and a bare or green (ground) wire. Take note of how these wires are connected to the existing outlet.
Step 4: Connect the Ground Wire
Connect the bare or green ground wire to the green grounding screw on the GFCI receptacle. Ensure it is securely tightened.
Step 5: Connect the Neutral Wire
Connect the white neutral wire to the silver (neutral) terminal on the GFCI receptacle.
Step 6: Connect the Hot Wire
Connect the black hot wire to the brass (hot) terminal on the GFCI receptacle.
Step 7: Install the Receptacle Back into the Box
Carefully push the wires back into the electrical box and secure the GFCI receptacle with screws.
Step 8: Replace the Faceplate
Attach the faceplate to the GFCI receptacle and ensure it is securely fastened.
Step 9: Turn the Power Back On
Return to the circuit breaker panel and turn the power back on. Use a voltage tester to ensure that the GFCI receptacle is receiving power.
Step 10: Test the GFCI Receptacle
Press the "Test" button on the GFCI receptacle. If it trips and cuts power, it is working correctly. Press the "Reset" button to restore power.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Not turning off the power before starting work.
- Incorrectly wiring the receptacle (hot and neutral reversed).
- Neglecting to test the GFCI after installation.
- Forgetting to secure all connections properly.
8. Case Studies and Real-World Examples
In 2020, a homeowner in Florida suffered a minor electrical shock while using a faulty outlet in their bathroom. After the incident, they installed GFCI receptacles in all moisture-prone areas. Following installation, they reported a significant decrease in electrical incidents, reinforcing the importance of GFCI installations.
9. Expert Insights and Tips
According to electrical safety experts, GFCI receptacles should be installed in any area exposed to water, including kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor locations. Additionally, regular testing of GFCI receptacles is recommended at least once a month to ensure they are functioning correctly.
10. FAQs
1. What is a GFCI receptacle?
A GFCI receptacle is an electrical outlet designed to protect against ground faults that could lead to electric shock.
2. Where should GFCI receptacles be installed?
They should be installed in areas where water and electricity may come into contact, such as bathrooms, kitchens, basements, and outdoors.
3. How do I know if my GFCI receptacle is working?
Press the "Test" button on the GFCI. If it trips and cuts power, it is functioning correctly. Reset it to restore power.
4. Can I install a GFCI receptacle myself?
Yes, as long as you follow safety precautions and local electrical codes. However, if you're unsure, consult a licensed electrician.
5. What happens if a GFCI receptacle fails?
If a GFCI receptacle fails, it may no longer trip when it should, increasing the risk of electrical shock. It should be replaced immediately.
6. How often should I test my GFCI receptacle?
It is recommended to test GFCI receptacles at least once a month to ensure they are working properly.
7. What is the difference between a standard outlet and a GFCI outlet?
A standard outlet does not provide ground fault protection, while a GFCI outlet monitors electrical flow and can shut off power in dangerous situations.
8. Can I use a GFCI outlet in place of a regular outlet?
Yes, GFCI receptacles can be used in place of regular outlets to provide additional safety.
9. Are GFCI receptacles required by code?
Yes, many local electrical codes require GFCI receptacles in specified areas of the home, especially where water is present.
10. How long do GFCI receptacles last?
GFCI receptacles typically last for 15-25 years, but they should be tested regularly and replaced if they fail.
By following this guide, you can safely wire a GFCI receptacle in your home, enhancing safety and compliance with electrical codes. For more detailed information, consider consulting the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) for guidelines on electrical safety and installation.
Random Reads