Mastering Your Mac: A Complete Guide to Finding Internal & External IP Addresses
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding IP Addresses
- What is an Internal IP Address?
- What is an External IP Address?
- How to Find Your Internal IP Address on a Mac
- How to Find Your External IP Address on a Mac
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Advanced Usage of IP Addresses
- Case Studies
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
In today's digital world, understanding your IP address is crucial for effective networking and online privacy. Whether you're troubleshooting connectivity issues or setting up a new device, knowing how to find your internal and external IP address on a Mac is essential. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process step-by-step, along with insights into what these addresses mean and their significance in your daily digital interactions.
Understanding IP Addresses
An IP address, or Internet Protocol address, is a unique identifier assigned to each device connected to a network. It serves two primary functions: identifying the host or network interface and providing the location of the device in the network. There are two types of IP addresses: internal (private) and external (public).
Types of IP Addresses
- Internal IP Address: This address is assigned to devices within a private network, such as your home network. It is not visible to the outside world.
- External IP Address: This address is assigned by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and is visible to external networks. It allows you to connect to the internet.
What is an Internal IP Address?
The internal IP address is used for communication between devices on a local network. It typically falls within specific ranges defined by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). Common internal IP address ranges include:
- 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
For example, if you are connected to your home Wi-Fi, your Mac might have an IP address like 192.168.1.2.
What is an External IP Address?
Your external IP address is what the rest of the internet sees when you connect to it. It is assigned by your ISP and can change frequently unless you have a static IP address. You can find your external IP by using various online tools or commands. It is essential for activities like accessing the internet and hosting servers.
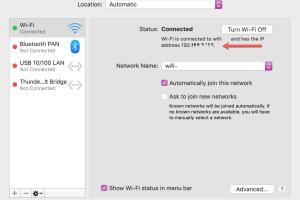
How to Find Your Internal IP Address on a Mac
Finding your internal IP address on a Mac is straightforward. Here are two methods you can use:
Method 1: Using System Preferences
- Click on the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen.
- Select System Preferences.
- Click on Network.
- Select your active network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) from the left pane.
- Your internal IP address will be displayed under the "Status" section. It typically looks like 192.168.x.x.
Method 2: Using the Terminal
- Open the Terminal application (you can find it in Applications > Utilities).
- Type the command
ifconfigand press Enter. - Look for the line that starts with inet under the section that corresponds to your active connection (usually en0 for Ethernet or en1 for Wi-Fi).
- Your internal IP address will be displayed next to the inet label.
How to Find Your External IP Address on a Mac
Finding your external IP address can be done easily using one of the following methods:
Method 1: Using a Web Service
- Open your web browser.
- Visit a site like WhatIsMyIP.com or IPInfo.io.
- Your external IP address will be displayed prominently on the page.
Method 2: Using the Terminal
- Open the Terminal application.
- Type the command
curl ifconfig.meand press Enter. - Your external IP address will be displayed in the Terminal window.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Sometimes, you may encounter issues while trying to find your IP address. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
Problem 1: Unable to Connect to Wi-Fi
If you can't connect to Wi-Fi, ensure that:
- Your Wi-Fi is turned on and you are within range of the network.
- You have the correct password.
- Your router is functioning properly.
Problem 2: IP Address Not Displaying
If your IP address isn't displaying, try restarting your system or router. If the problem persists, check your network settings.
Advanced Usage of IP Addresses
Understanding IP addresses can also help with advanced networking tasks, such as:
- Setting up a local server for development.
- Configuring port forwarding on your router.
- Using VPNs for enhanced privacy and security.
Case Studies
Consider the following examples to understand the implications of internal and external IP addresses:
Case Study 1: Home Network Setup
A family sets up a home network with multiple devices. They use internal IP addresses to manage device communication while relying on an external IP address for internet access. Understanding these addresses helped them troubleshoot connectivity issues.
Case Study 2: Remote Work Security
A remote worker uses a VPN to secure their external IP address while accessing company resources. This highlights the importance of IP addresses in maintaining privacy and security in professional environments.
Conclusion
Finding your internal and external IP address on a Mac is an essential skill for anyone looking to understand their network better. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can easily locate your IP addresses and troubleshoot any networking issues you may encounter.
FAQs
- What is the difference between internal and external IP addresses?
Internal IP addresses are used within a private network, while external IP addresses are used to communicate over the internet. - Can my external IP address change?
Yes, most ISPs assign dynamic external IP addresses that can change periodically. - How can I secure my external IP address?
Using a VPN is a great way to mask your external IP address and enhance your online privacy. - What should I do if I cannot find my internal IP address?
Check your network connection settings or restart your router and device. - Is it possible to have multiple external IP addresses?
Yes, businesses may have multiple external IP addresses for different services or locations. - How often should I check my IP address?
Regular checks are not necessary, but you should verify it when troubleshooting connectivity issues. - Can I change my internal IP address?
Yes, you can manually set a static internal IP address through your network settings. - What is a static vs dynamic IP address?
A static IP address remains the same, while a dynamic IP address can change over time. - Can I find my external IP address without using a web service?
Yes, you can use Terminal commands likecurl ifconfig.me. - Why does my internal IP address start with 192.168?
This is a common range for internal IP addresses assigned by routers for home networks.
Random Reads