Ultimate Guide to Measuring Voltage: Techniques, Tools, and Tips
-
Quick Links:
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Understanding Voltage
- 3. Importance of Measuring Voltage
- 4. Tools for Measuring Voltage
- 5. Types of Voltage Measurements
- 6. How to Measure Voltage
- 7. Case Studies
- 8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 9. FAQs
- 10. Conclusion
1. Introduction
Voltage measurement is a fundamental aspect of electrical engineering and everyday electronics. Understanding how to measure voltage accurately can help prevent electrical failures, ensure safety, and maintain system efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different methods and tools used for measuring voltage, delve into their applications, and provide step-by-step instructions for accurate measurements.
2. Understanding Voltage
Voltage, also known as electric potential difference, is the measure of electric potential energy per unit charge. It is what drives electric current through a circuit. Voltage is measured in volts (V) and is essential for understanding how electrical devices operate.
2.1 What is Voltage?
Voltage can be thought of as the pressure that pushes electric charges through a conducting loop. It is created by differences in electric potential between two points in a circuit. The greater the difference in potential, the higher the voltage.
2.2 Types of Voltage
- AC Voltage: Alternating current voltage changes direction periodically. Commonly found in household outlets.
- DC Voltage: Direct current voltage flows in one direction, typically produced by batteries.
3. Importance of Measuring Voltage
Measuring voltage is crucial for various reasons:
- Ensures electrical systems operate within safe limits.
- Helps diagnose electrical issues in devices.
- Facilitates maintenance and troubleshooting.
4. Tools for Measuring Voltage
Several tools can be used to measure voltage, each with its own advantages and use cases:
- Multimeter: A versatile tool that can measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Voltmeter: Specifically designed to measure voltage in a circuit.
- Oscilloscope: Used for visualizing voltage waveforms over time.
5. Types of Voltage Measurements
Voltage can be measured in several ways depending on the application:
- Absolute Voltage Measurement: Measuring the voltage at a specific point relative to a common reference (usually ground).
- Relative Voltage Measurement: Measuring voltage between two points in a circuit.
6. How to Measure Voltage
Measuring voltage can be accomplished in a few simple steps:
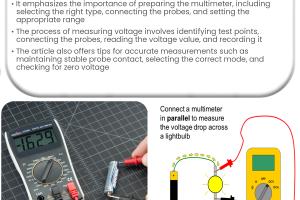
6.1 Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Multimeter
- Set Up the Multimeter: Turn the multimeter on and set the dial to the voltage measurement mode (AC or DC).
- Connect the Probes: Insert the black probe into the COM terminal and the red probe into the VΩmA terminal.
- Measure Voltage: Touch the black probe to the ground or negative terminal, and the red probe to the positive terminal. Read the voltage on the display.
6.2 Measuring Voltage with a Voltmeter
- Follow similar steps as the multimeter but ensure the voltmeter is in the correct voltage setting.
- Connect the probes to the circuit as described above.
6.3 Safety Precautions
Always ensure safety when measuring voltage:
- Wear insulated gloves and goggles.
- Be cautious of high voltages.
- Ensure the multimeter is rated for the voltage being measured.
7. Case Studies
Understanding voltage measurement through real-world applications can provide valuable insights:
7.1 Case Study: Household Electrical Systems
In a typical household, measuring voltage is essential for troubleshooting electrical issues. For instance, if a light fixture is flickering, measuring the voltage at the fixture can determine if there are fluctuations that might be causing the problem.
7.2 Case Study: Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, voltage measurements are crucial for maintaining equipment. For example, measuring the voltage of motors ensures they operate efficiently and do not draw excess current, which can lead to overheating and failure.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
When measuring voltage, some common mistakes can occur:
- Using the wrong setting on the multimeter.
- Failing to connect probes correctly.
- Not considering the frequency of AC voltage measurements.
9. FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between AC and DC voltage?
A1: AC (Alternating Current) voltage changes direction periodically, while DC (Direct Current) voltage flows in one direction.
Q2: Can I measure AC voltage with a DC multimeter?
A2: No, a DC multimeter is designed for measuring direct current only. Use an AC voltmeter or a multimeter that supports AC measurements.
Q3: What safety precautions should I take?
A3: Always wear insulated gloves, avoid touching live wires, and ensure your multimeter is rated for the voltage levels you are measuring.
Q4: How do I know if my multimeter is functioning correctly?
A4: Test the multimeter on a known voltage source, such as a battery, to ensure it provides the correct reading.
Q5: What is the highest voltage I can measure safely?
A5: This depends on the rating of your multimeter. Most consumer-grade multimeters can measure up to 600V, while specialized ones can measure higher voltages.
Q6: What happens if I connect the probes incorrectly?
A6: Connecting the probes incorrectly can result in inaccurate readings or damage to the multimeter. Always double-check connections before measuring.
Q7: Can I measure voltage in a live circuit?
A7: Yes, but ensure you take necessary precautions and use a multimeter rated for live measurements.
Q8: What tools do I need to measure voltage?
A8: A multimeter or voltmeter is essential for measuring voltage. An oscilloscope can also be used for detailed waveform analysis.
Q9: How do I interpret the readings on my multimeter?
A9: The display will show the voltage in volts (V). Ensure you understand the scale (AC vs. DC) when interpreting the results.
Q10: What are the common applications for voltage measurement?
A10: Voltage measurements are used in diagnostics, maintenance, and testing of electrical equipment, circuits, and systems.
10. Conclusion
Understanding how to measure voltage is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems. By following the techniques and safety precautions outlined in this guide, you can improve your skills and ensure accurate measurements in any application. Whether for professional or personal use, mastering voltage measurement will enhance your electrical knowledge and capabilities.
References:
- Electronics Tutorials on Voltage Measurement
- NI on Understanding Voltages
- Fluke on Voltage Measurement in Electrical Systems
Random Reads
- Remove incognito mode chrome android
- How to make fake error message windows
- How to make friends with famous people
- How to use 7 zip compress files
- How to use a calling card
- Remove user accounts windows 10
- How to open new window in web browser
- How to wire an electric dryer
- How to woohoo in the sims 2
- How to remove mold stains from wood floors