Mastering Series Circuits: Step-by-Step Solutions for Beginners
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- Understanding Series Circuits
- Ohm's Law Explained
- How to Solve a Series Circuit
- Case Studies and Real-World Applications
- Expert Insights
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction
Series circuits form the bedrock of electrical engineering and are essential for anyone looking to understand how electrical systems operate. Whether you’re a student, a DIY enthusiast, or just curious about electronics, mastering series circuits is a vital skill. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the principles governing series circuits, provide step-by-step solutions, and explore real-world applications.
Understanding Series Circuits
A series circuit is a type of electrical circuit in which components are connected end-to-end, forming a single path for current to flow. If any component fails or is disconnected, the entire circuit stops functioning. Understanding the characteristics of series circuits is crucial for solving them effectively.
- Components: Typically includes resistors, capacitors, and power sources.
- Current: The same current flows through all components.
- Voltage: The total voltage across the circuit is the sum of the voltages across each component.
- Resistance: The total resistance is the sum of individual resistances.
Ohm's Law Explained
Ohm's Law is fundamental to solving circuits. It states that:
V = I × R
- V: Voltage (Volts)
- I: Current (Amperes)
- R: Resistance (Ohms)
Understanding how to manipulate this equation will enable you to analyze and solve series circuits effectively.
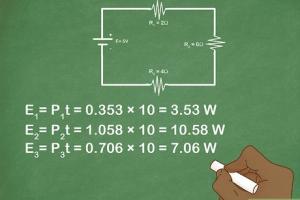
How to Solve a Series Circuit
Solving a series circuit involves the following steps:
Step 1: Identify the Components
Begin by listing all components in the circuit, including resistors, capacitors, and the voltage supply.
Step 2: Calculate Total Resistance
Use the formula:
Rtotal = R1 + R2 + R3 + ...
For example, if you have three resistors in series: R1 = 2Ω, R2 = 3Ω, and R3 = 5Ω, then:
Rtotal = 2 + 3 + 5 = 10Ω
Step 3: Determine Total Voltage
Measure or identify the total voltage supplied by the battery or power source.
For instance, if your power source is a 12V battery, then Vtotal = 12V.
Step 4: Apply Ohm's Law to Find Current
Use Ohm's Law to calculate the current flowing through the circuit:
I = Vtotal / Rtotal
For our example:
I = 12V / 10Ω = 1.2A
Step 5: Calculate Voltage Across Each Component
To find the voltage drop across each resistor, use:
VR = I × R
- For R1: V1 = 1.2A × 2Ω = 2.4V - For R2: V2 = 1.2A × 3Ω = 3.6V - For R3: V3 = 1.2A × 5Ω = 6V
Step 6: Verify the Circuit
Ensure that the sum of the voltage drops equals the total voltage:
2.4V + 3.6V + 6V = 12V
If this is true, your calculations are correct!
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Understanding theory is essential, but real-world applications of series circuits bring the concepts to life.
Case Study 1: Christmas Lights
Many Christmas light strings are wired in series. If one bulb goes out, the entire string goes dark. This illustrates the importance of understanding series circuits in practical scenarios.
Case Study 2: Battery Packs
Battery packs often connect several cells in series to achieve higher voltage levels. For instance, connecting six 1.5V batteries in series will yield a total of 9V.
Expert Insights
According to Electronics Tutorials, series circuits are vital in applications where the same current must flow through multiple components, such as in LED lighting and simple electronic devices.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Forget to sum total resistance correctly.
- Overlook the voltage drop across each component.
- Neglect the effect of internal resistance in batteries.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of solving series circuits is an essential skill for anyone delving into electrical engineering. By following the systematic approach outlined in this guide, you can confidently analyze and understand series circuits, paving the way for more complex electrical concepts.
FAQs
-
What is a series circuit?
A series circuit is a circuit where components are connected end-to-end, allowing current to flow through one path.
-
How do you calculate total resistance in a series circuit?
Total resistance is the sum of all individual resistances: Rtotal = R1 + R2 + ...
-
What happens if one component fails in a series circuit?
If one component fails, the entire circuit is interrupted and stops functioning.
-
Can you have a series circuit with different voltage ratings?
Yes, but ensure the total voltage does not exceed the limits of any component.
-
What is the significance of Ohm's Law in series circuits?
Ohm's Law helps to calculate the current, voltage, and resistance in the circuit.
-
Are series circuits used in household wiring?
No, household wiring typically uses parallel circuits to ensure that devices can operate independently.
-
What are some common applications of series circuits?
Common applications include battery-powered devices, LED lights, and simple electronic toys.
-
How do I measure current in a series circuit?
Use an ammeter connected in series to measure the current flowing through the circuit.
-
Can series circuits be dangerous?
Yes, if not designed properly, they can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
-
How can I practice solving series circuits?
Work on practice problems, use circuit simulators, or build simple circuits on a breadboard.
Random Reads
- How to remove mold mildew front loading washer gasket
- Two simple ways to reboot an ipad
- How to delete whatsapp message before reading
- How to delete yahoo account
- How to update download java
- How to update graphics card
- Delete temporary prefetch files
- Delete tables in word
- Ultimate guide installing bx electrical cables
- How to contact seller on amazon