Mastering the Art of Reading Schematics: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
-
Quick Links:
- 1. Introduction to Schematics
- 2. Understanding Schematic Symbols
- 3. Types of Schematics
- 4. Basic Components in Schematics
- 5. Reading Schematics Step-by-Step
- 6. Case Studies of Reading Schematics
- 7. Expert Insights on Schematics
- 8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 9. Resources for Further Learning
- 10. FAQs
1. Introduction to Schematics
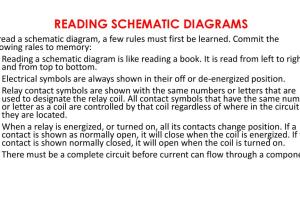
Schematics serve as the blueprint for electronic devices, providing a visual representation of the electrical connections and components. Understanding how to read these diagrams is crucial for anyone involved in electronics, whether you're a hobbyist, student, or professional. This guide aims to demystify schematics and equip you with the skills needed to interpret them with confidence.
2. Understanding Schematic Symbols
Every schematic uses standardized symbols to represent various electronic components. Knowing these symbols is the first step in learning how to read schematics effectively.
Schematic Symbol Examples
- Resistor: A zigzag line or rectangle, showing resistance in a circuit.
- Capacitor: Two parallel lines, indicating energy storage.
- Diode: A triangle pointing toward a line, illustrating current flow direction.
These symbols are universally recognized, making it easier for engineers and technicians worldwide to communicate ideas and designs.
3. Types of Schematics
Schematics can be categorized into several types based on their purpose and complexity:
- Block Diagrams: Simplified representations showing major components and their relations.
- Circuit Diagrams: Detailed representations that provide complete information about components and connections.
- Wiring Diagrams: Specific diagrams that show how to physically wire components.
4. Basic Components in Schematics
Understanding the basic components is essential for reading schematics. Here are the most common components that you'll encounter:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Resistor | Limits current flow |
| Capacitor | Stores electrical energy |
| Inductor | Stores energy in a magnetic field |
| Transistor | Acts as a switch or amplifier |
5. Reading Schematics Step-by-Step
Now that you understand the symbols and components, let's walk through the process of reading a schematic step-by-step:
- Identify the Power Source: Locate where the power enters the circuit.
- Trace the Path: Follow the connections from the power source through the components.
- Understand the Function: Analyze how each component contributes to the circuit's overall function.
- Verify Connections: Check for correct connections to avoid errors in assembly.
6. Case Studies of Reading Schematics
Real-world examples can reinforce your understanding of schematics. Consider the following case studies:
Case Study 1: Basic LED Circuit
In a simple LED circuit, the schematic shows a power source connected to a resistor and an LED. By following the path, you can see how current flows through the resistor to limit the current and then to the LED, allowing it to light up.
Case Study 2: Amplifier Circuit
This more complex schematic includes transistors, resistors, and capacitors. By analyzing the interconnections, you can understand how the input signal is amplified before being output.
7. Expert Insights on Schematics
Experts recommend practicing with various schematics to improve your skills. Start with simple circuits and gradually move to more complex designs. Online forums and communities can provide valuable feedback and insights.
Additionally, tools like simulation software can help visualize how circuits function without the need for physical components.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid
When reading schematics, it's easy to make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls:
- Ignoring the power source orientation.
- Assuming all components are the same; double-check specifications.
- Failing to trace connections thoroughly.
9. Resources for Further Learning
Here are some valuable resources to deepen your understanding of schematics:
- Electronics Tutorials - Comprehensive guides on electronic principles.
- Khan Academy - Free courses on electrical engineering topics.
- SparkFun - Educational resources and kits for hands-on learning.
10. FAQs
What is a schematic diagram?
A schematic diagram is a visual representation of an electrical circuit, showing how components are connected.
Why are schematic symbols important?
Schematic symbols provide a universal language in electronics, allowing engineers and technicians to communicate effectively.
How can I practice reading schematics?
Start with simple circuit diagrams and gradually progress to more complex designs. Use simulation software for practice.
Are there different types of schematics for different professions?
Yes, schematics can vary between electrical engineering, automotive, and other fields, each using specific symbols and layouts.
What tools do I need to read schematics?
Basic tools include a multimeter, soldering iron, and schematic drawing software for creating or analyzing circuits.
Can I learn to read schematics without formal training?
Absolutely! Many resources are available online for self-study, including tutorials, videos, and forums.
What are some common mistakes when reading schematics?
Common mistakes include misreading symbols, overlooking connections, and not verifying component values.
Is there software available to help with reading schematics?
Yes, there are many software options, such as Eagle, KiCAD, and Fritzing, that can help you design and analyze schematics.
How can I improve my schematic reading skills?
Practice regularly, participate in electronics projects, and engage with the online community to learn from others.
Where can I find more advanced schematics?
Explore electronics forums, educational websites, and manufacturer datasheets for more complex schematic examples.
Random Reads
- Safely get rid of empty paint cans
- How to install bathroom sink
- How to install broadband
- How to view source code
- Mastering laptop battery discharge
- How to play multiplayer minecraft xbox 360
- How to play minesweeper
- How to install adobe acrobat reader
- How to install a septic system
- How to keep birds off your porch