Unlocking Windows: A Complete Guide to Finding User SID
-
Quick Links:
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Understanding Security Identifiers (SIDs)
- 3. Why You Might Need to Find a User's SID
- 4. Methods to Find a User's SID
- 5. Using Command Prompt to Find SID
- 6. Using PowerShell to Find SID
- 7. Finding SID with Visual Studio
- 8. Case Studies and Real-World Applications
- 9. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- 10. FAQs
1. Introduction
Understanding how to find a user's Security Identifier (SID) on Windows is crucial for system administrators, developers, and advanced users. The SID is a unique string that identifies each user account in Windows, enabling the operating system to manage permissions and security settings effectively. In this guide, we'll delve into various methods to locate a user’s SID, providing step-by-step instructions, expert insights, and real-world examples.
2. Understanding Security Identifiers (SIDs)
A Security Identifier (SID) is a unique value used to identify a security principal or security group in Windows operating systems. It is essential for managing user access to resources and is integral to Windows security architecture. Each SID is composed of a series of numbers and letters, formatted in a specific way.
- Structure: A SID typically looks like this:
S-1-5-21-. - Importance: SIDs ensure that permissions are assigned and managed securely across the system.
3. Why You Might Need to Find a User's SID
There are several scenarios in which locating a user's SID becomes necessary:
- Configuring user permissions
- Auditing security settings
- Transferring user profiles
- Diagnosing user access issues
4. Methods to Find a User's SID
There are multiple methods to find a user's SID, including:
- Using Command Prompt
- Using PowerShell
- Using graphical user interfaces like Local Users and Groups
- Using third-party software tools
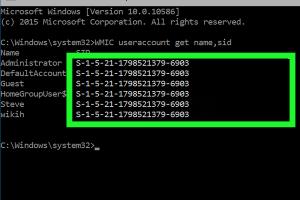
5. Using Command Prompt to Find SID
The Command Prompt is a powerful tool that can be used to find a user's SID. Follow these steps:
- Press
Windows + Rto open the Run dialog. - Type
cmdand hitEnter. - In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press
Enter:wmic useraccount where name='username' get sid. - Replace
usernamewith the actual username you wish to find the SID for.
The output will display the SID associated with that username.
6. Using PowerShell to Find SID
PowerShell is a more advanced tool that provides additional functionality compared to the Command Prompt. Here’s how to use it to find a user's SID:
- Press
Windows + Xand selectWindows PowerShell. - Type the following command and press
Enter:Get-LocalUser -Name 'username'. - Look for the
SIDattribute in the output.
7. Finding SID with Visual Studio
If you are a developer and already using Visual Studio, you can retrieve a user's SID programmatically. Below is a simple example in C#:
using System;
using System.Security.Principal;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
WindowsIdentity identity = WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent();
Console.WriteLine(identity.User.Value);
}
}
This code retrieves the SID of the currently logged-in user.
8. Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Understanding how to find a user's SID can be applied in various real-world scenarios. Here are a few case studies:
- Case Study 1: A system administrator needed to migrate user accounts from one domain to another. Knowing the SID allowed for seamless permissions transfer.
- Case Study 2: A developer troubleshooting access issues for an application found that the application's permissions were incorrectly set due to a wrong SID.
9. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Here are some common issues users face when trying to find a user's SID, along with troubleshooting tips:
- Access Denied: Ensure you have administrative privileges to run the commands.
- User Not Found: Double-check the username for typos.
- Command Not Recognized: Ensure you are using the correct syntax for the command.
10. FAQs
1. What is a SID?
A Security Identifier (SID) is a unique value used to identify a security principal or group in Windows.
2. Why do I need a user's SID?
SIDs are essential for managing user permissions and security settings in Windows.
3. Can I find the SID for a deleted user?
No, once a user is deleted, their SID is also removed from the system.
4. Is it possible to change a user's SID?
No, SIDs are immutable once assigned to a user account.
5. What tools can I use to find a user's SID?
You can use Command Prompt, PowerShell, or graphical tools like Local Users and Groups.
6. How do I find the SID for a group?
Use the same methods as finding a user’s SID, just specify the group name instead.
7. Are SIDs visible in the Windows registry?
Yes, SIDs can be found under certain registry keys, particularly in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/SOFTWARE/Microsoft/Windows NT/CurrentVersion/ProfileList.
8. Can I use third-party tools to find SIDs?
Yes, various third-party software tools can help you retrieve SIDs, but ensure they are from trusted sources.
9. What if I get an error while using Command Prompt?
Check for typos in the command and ensure you have the necessary permissions.
10. How can I verify the SID I found is correct?
Cross-reference the SID with the user account settings in the Local Users and Groups management console.
Random Reads